Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
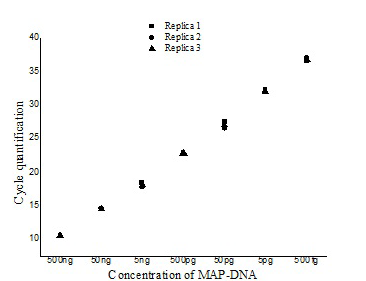
Figure 1: Intra-assay variability
Figure illustrating the variation with in the three replicates of serially diluted MAP-DNA from 500ng to 50 fg analysed in the same run (■- Replica1, ●– Replica 2, ▲- Replica 3).
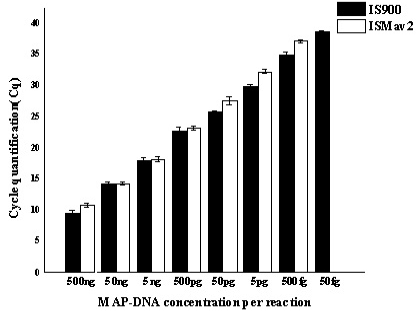
Figure 2: Reproducibility study of Inter-assay variability Serially diluted MAP-DNA analysed in triplicates on three different days, by using both IS900 and ISMav2 gene targets. Mean of the three different days were plotted with Standard deviation.
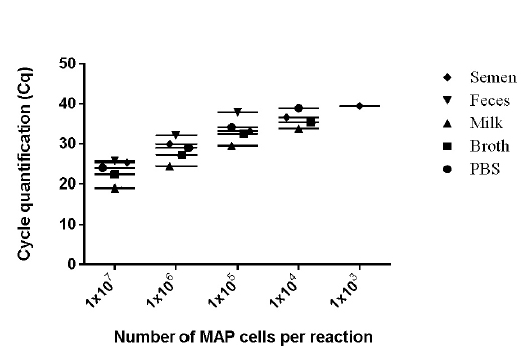
Figure 3: Detection limits of MAP K-10 (ATCC)
Strain were diluted in various clinical and chemical matrices. 1X107 to 1X101 MAP cells/ml were spiked in different matrices (Semen, Milk, Phosphate buffered saline, and Middlebrook 7H9 Broth). Whereas 1X107 to 1X101 MAP cells were spiked per gram of feces. Mean of the three days were plotted in graph. The number of M. avium subsp paratuberculosis (MAP) organisms per/reaction is shown on X-axis and CT values are on the Y-axis (●- PBS, ■ - Broth, ♦- Semen, ▲- Milk, ▼- Feces).
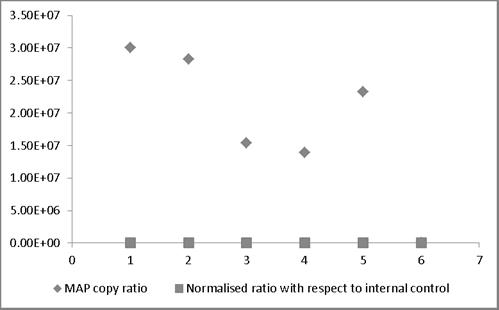
Figure 4: Normalization of quantified MAP copy number by exogenous internal control
MAP copy ratio = copy number of sample before normalization/ copy number of sample with lowest copy normalization; Normalized ratio = copy number of sample after normalization/ copy number of sample with lowest copy after normalization. Most of the normalized Ct values expressed as ratio lie around 1 providing a truer representation compared to those values not normalized and therefore representing larger variation.