Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
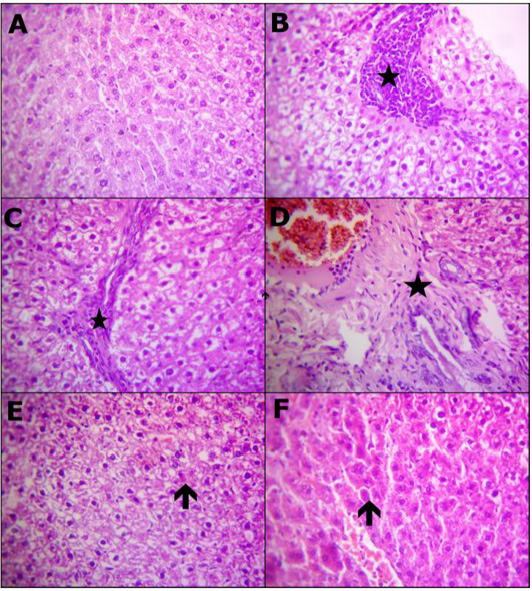
Reprehensive photomicrograph of rats liver (H and E, X400) showing; (A) Normal hepatic micromorphological structures; (B) Necrosis hepatocytes replaced by inflammatory aggregations (star); (C) Interlobular fibrotic strands (star); (D) Portal fibrosis besides congested blood vessels and proliferated bile duct epithelium (star); (E) Restore normal hepatocytes and heperplastic Kupffer cells with a few hepatocytes appeared apoptosis (arrow); (F) Apparently normal hepatocytes with prominent diplocytes (arrow) with still slight congested blood vessels. (A) Control; (B, C and D) Lead toxicity; (E) Lead + Cranberry (75mg), Lead + Cranberry (150mg) n=10.
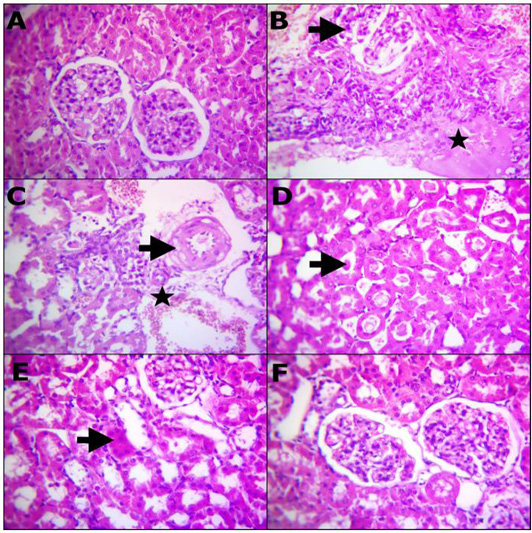
Reprehensive photomicrograph of rats Kidney (H and E, X400) showing; (A) Normal renal histomorphological structures; (B) Massive necrotic renal tubules and glomeruli (arrow) besides edema infiltrated with inflammatory cells (star); (C) Degenerated renal tubules, interstitial inflammatory cells infiltrarions, extravasated erythrocytes (star) and vasculitis characterized by endotheliosis and vacuolar media (arrow); (D) Prominent homogenous more eosinophilic cats in the convoluted renal tubules (arrow); (E) Remodeling the majority renal structures with regenerated attapts (arrow); (F) Apparently normal renal glomeruli and proximal tubules. (A) Control; (B, C and D) Lead toxicity; (E) Lead + Cranberry (75mg), Lead + Cranberry (150mg) n=10.