Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
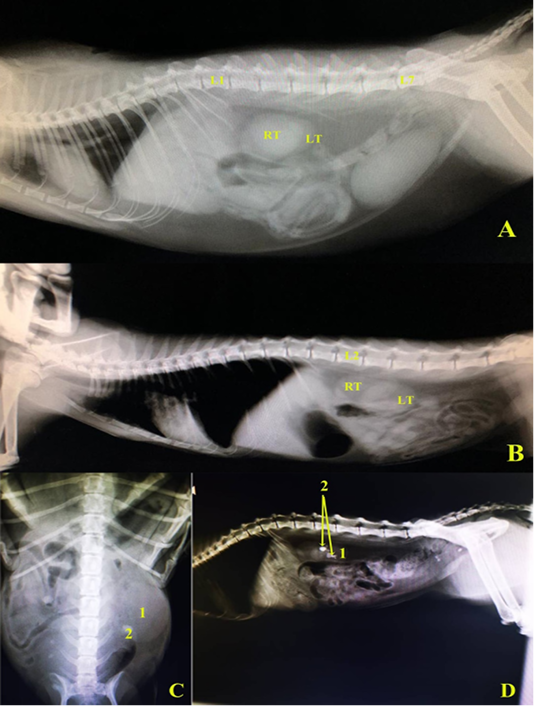
A and B, left lateral radiographic view in two domestic cats showing the normal positions of right and left kidneys. C, Ventrodorsal radiographic view showing enlarged left kidney (hydronephrosis), D, left lateral radiographic view showing renal calculi in left kidney, in domestic cats. L1.1st lumber vertebra, L2.2nd lumber vertebra, L7. 7th lumber vertebra, RT right kidney, LT.left kidney, 1 left kidney (hydronephrotic in C), 2. Renal calculus.
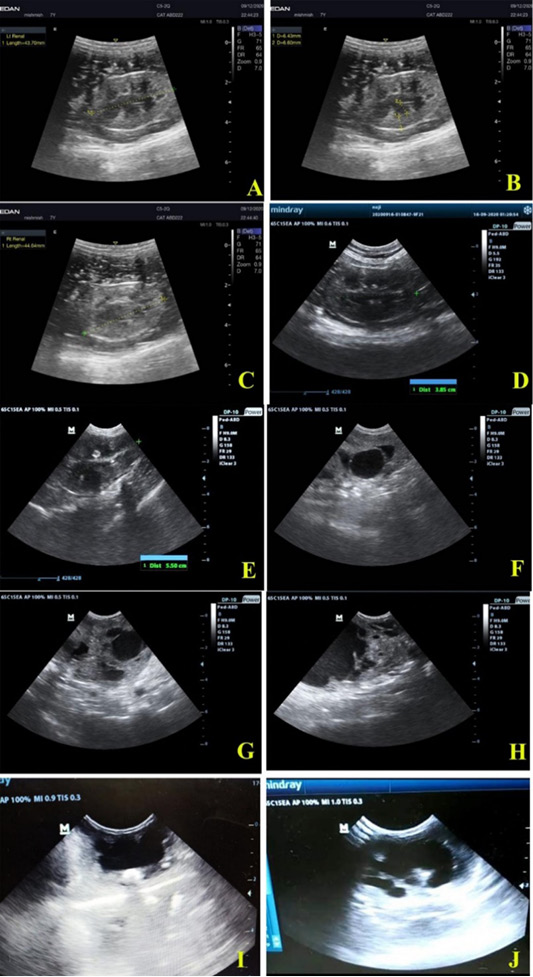
Ultrasonographic views of healthy feline kidneys showing. A, Left kidney with length 4.37 cm; B, left renal cortex (0.64 cm), renal medulla (0.66 cm); C, right kidney length 4.46 cm; D, left kidney of another cat with length 3.85 cm. Feline unilateral hydronephrosis cases showing; E, enlarged right kidney (5.50 cm length); F, loss of architecture and dilated renal pelvis of right kidney in two years old mixed breed tomcat; G and H, loss of echotexture with multiple diverticuli in right kidney of 1 year old mixed breed queen; I, severe dilation of renal pelvis with thinning of renal cortex and medulla; J, massive loss of architecture with normal dimensional left kidney in 3 months old tomcat.
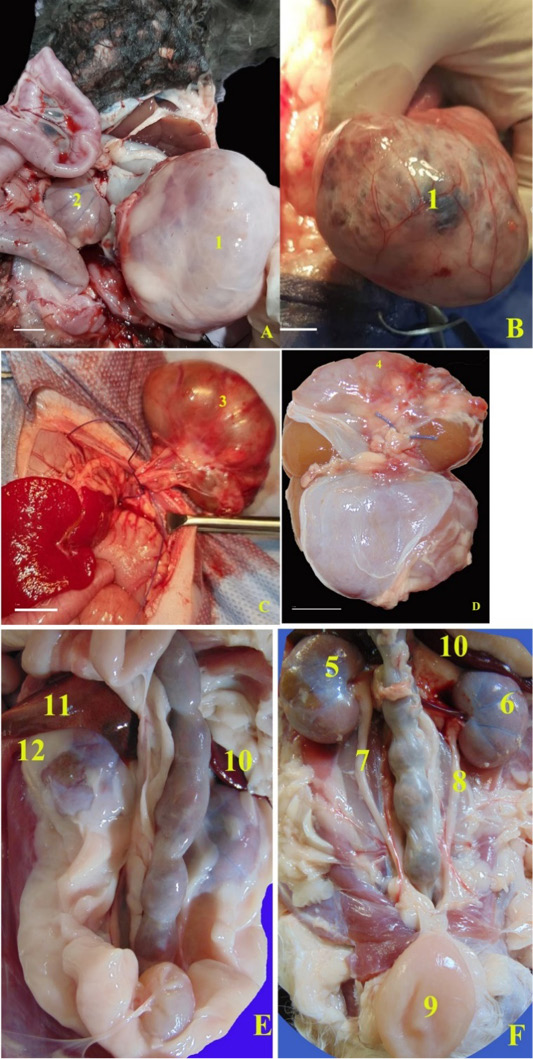
Unilateral hydronephrotic kidneys collected from two cases. A and B, the right kidney extremly enlarged; C and D, the hydronephrotic left kidney was collected after nephroctomy surgery. In healthy cats, E, F, Anatomical photographs of the ventrodorsal view of the abdominal cavity of healthy domestic cat, B, after removal of the perirenal fat. 1, Right hydronephrotic kidney; 2, Left small kidney; 3, left hydronephrotic kidney; 4, Adhesions in the renal capsule to the renal cortex of hydronephrotic kidney; 5, right kidney; 6, left kidney; 7, right ureter; 8, left ureter; 9, urinary bladder; 10, spleen; 11, caudate lobe; 12, capsula adiposa.
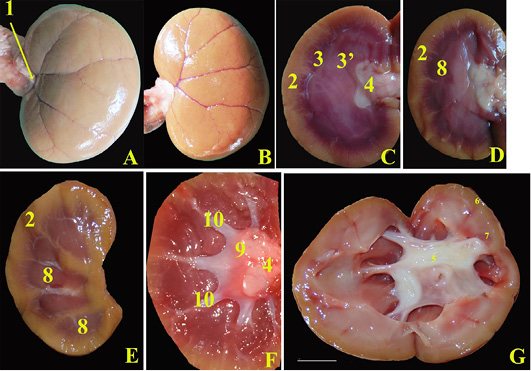
Anatomical photographs showing, Healthy kidneys; A, Separated Left kidney ventral surface cat after removal of the renal capsule; B, Dorsal surface of right kidney; C, the mid sagittal section; D, parasagittal section; E and F, sagittal sections. In diseased cat; D, midsagittal section of left hydronephrotic kidney with normal size. 1, renal hilus; 2, renal cortex; 3, outer renal medulla; 3, inner renal medulla; 4, normal renal pelvis; 5, Dilated renal pelvis due to hydronephrosis; 6, Renal cortex reduced in thickness; 7, Renal medulla reduced in thickness; 8, renal pyramid; 9, renal crest; 10, collateral recesses.
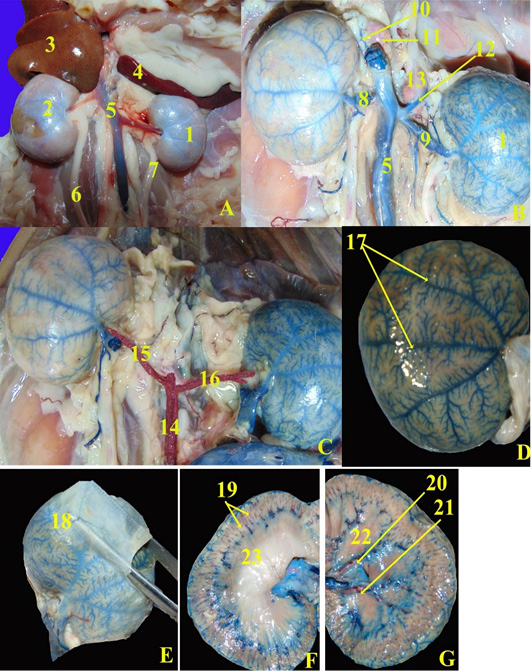
Anatomical magnified of the ventrodorsal view of the abdominal cavity of domestic healthy cat. A, Fresh specimen; B and C, Fresh specimen injected with blue and red latex neoprene; D, refleccted renal capsule (dorsal surface of right kidney); E, showing the content of fibrous capsule; F, midsagittal section; F, sagittal section. 1, left kidney; 2, right kidney; 3, caudate lobe of liver; 4, spleen; 5, caudal vena cava; 6, right ureter; 7, left ureter; 8, right renal vein; 9, left renal vein; 10, right adrenal vein; 11, right adrenal gland; 12, left adrenal vein; 13, left adrenal gland; 14, abdominal aorta; 15, right renal artery; 16, left renal artery; 17, subcapsular veins; 18, capsular veins; 19, interlobular arteries; 20, interlobar artery; 21, interlobar viens; 22, renal pyramid.