Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
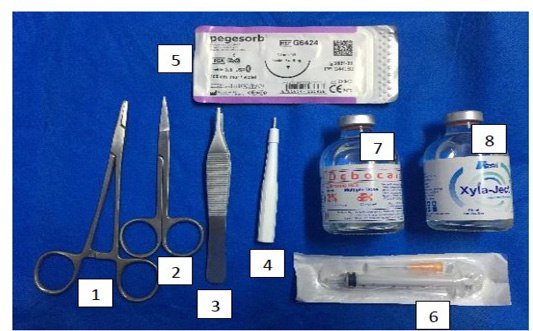
Skin punch biopsy Kit [(1) needle holder (2) scissor (3) tissue forceps (4) punch biopsy blade (5) vicryl suture filament (7) Lidocaine (8) xylazine
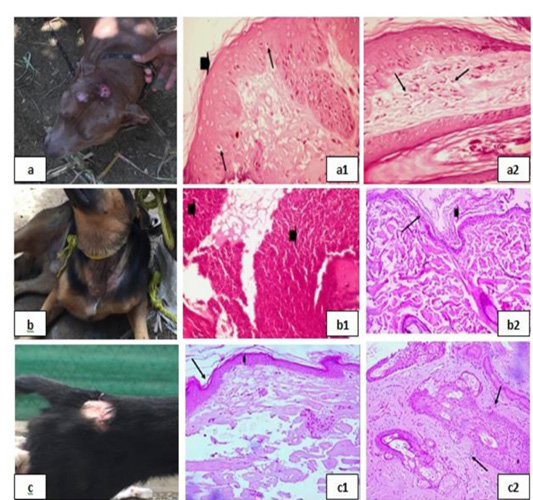
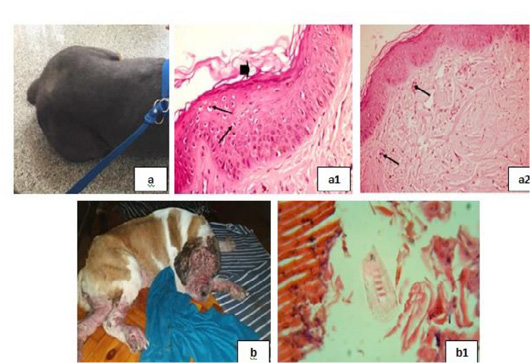
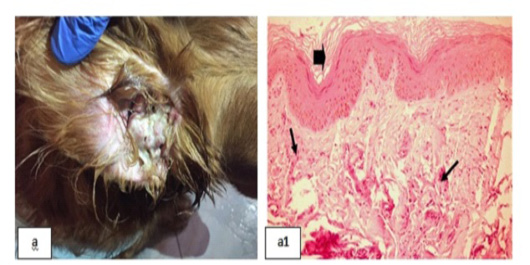
Bacterial infection dermopathies showing; 2a: Erythema and hair loss in the front of the head. 2(a1): keratolysis (arrow head) and spongiosis (arrows), (H&E X 200). 2(a2): Eosinophilic dermatitis with accumulation of eosinophils in the dermal layer (arrows), (H&E X 200).
2b: Traumatic dermatitis with secondary bacterial infection.
2(b1): Lymphocytic dermatitis (arrows), (H&E X 200). 2(b2): Keratolysis (arrow head) and acantholysis (arrow), (H&E X 200). 2c: Superficial pyoderma and ulcer formation. 2(c1), (c2): Lymphocytic dermatitis (arrows), (H&E X 200).
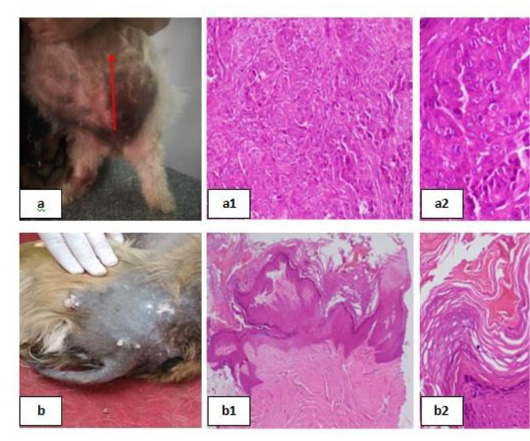
Erythematous lesions with hair loss alopecic areas showing; 3a: Erythematous lesions in the right elbow.
3(a1): Acanthosis and spongios (arrows), (H&E X 200).
3(a2): Perivascular Lymphocytic dermatitis (arrows), (H&E X 200). 3b: Erythematous lesions in the back. 3(b1): Ulceration (arrows), (H&E X 200). 3(b2): keratolysis (arrow head) and acantholysis (arrows), (H&E X 200).
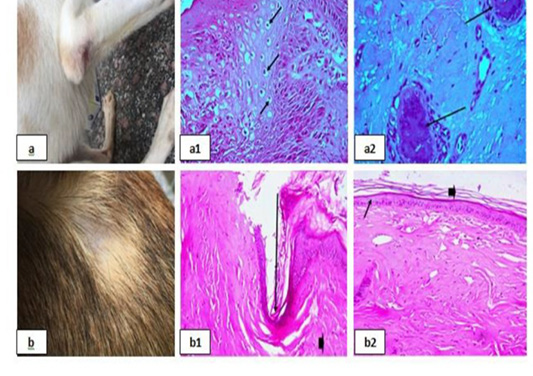
Parasitic infestations 1 showing; 4a, 4b: Flea allergic dermatitis (FAD) with pruritic lesion on the left trunk. 4(a1): Lymphocytic dermatitis (arrows), (H&E X 200). 4(a2), (b1): Ulceration (arrows), (H&E X 200). 4(b2): Necrotic hair follicle, (H&E X 200).
Parasitic infestations 2 showing; 5a: Flea allergic dermatitis (FAD) with pruritic lesion on the left trunk. 5(a1): Keratolysis (arrow head) and spongiosis (arrows), (H&E X 200). 5(a2): Eosinophilic dermatitis (arrows), (H&E X 200). 5b: Pyodemodicosis 5(b1): Demodex, (H&E X 200).
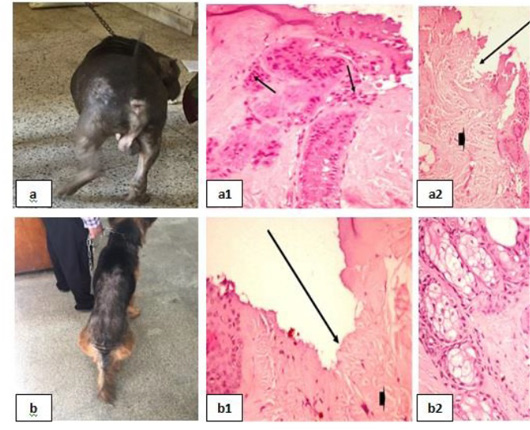
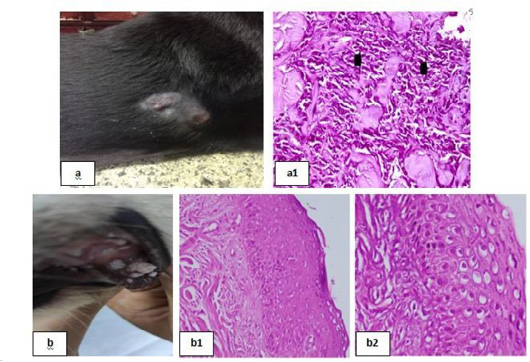
Skin tumors 1 showing; 6a: Soft subcutaneous lumps. 6(a1): Sarcoma cell tumor in the dermal layer with sheets of malignant cells, note the pleomorphism, hyperchromacia, increase nucleous : cytoplasmic ratio (arrow head), (H&E X 200). 6b: Cutaneous papillomatosis in the mouth 6(b1): Hyperplastic epidermis supported by fibrovascular tissue in the dermis, (H&E X 200). 6(b2): Irregular intracytoplasmic keratohyaline granules, (H&E X 200).
Skin tumors 2 showing; 7a: Mammary solid adenocarcinoma 7(a1): Carcinoma, solid type, (H&E X 200). 7(a2): Pleomorphic cells, hyperchromatic nuclei, central prominent nucleolus, and frequently detected mitosis, (H&E X 200). 7b: Canine papilloma, 7(b1): Hyperplastic epidermis , (H&E X 200). 7(b2): Prominent hyperkeratosis , (H&E X 200).
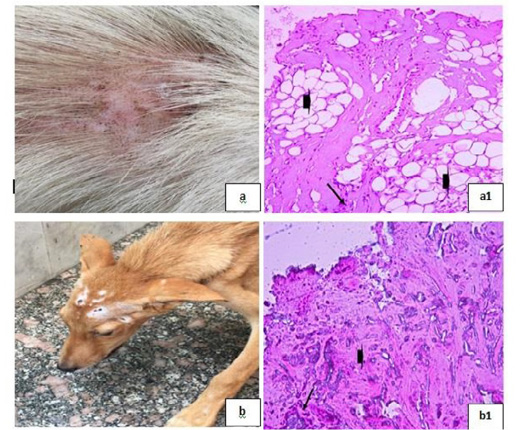
Dermatophytosis showing; 8a: Dermatophytosis with surface pyoderma and non-pruritic alopecia 8(a1): Lymphocytic dermatitis (arrow), with increased number of adipose cells (arrow head), (H&E X 200). 8b: Dermatophytosis with surface pyoderma and circumscribed white patches 8(b1): Necrotic dermatitis with sever necrosis in the dermal layer (arrow head) and leucocytic cells infiltrations (arrow), (H&E X 200).
Chronic Otitis externa showing; 9a: Red inflamed ear. 9(a1): Dyskeratosis (arrow head) and eosinophilic dermatitis (arrows), (H&E X 200).
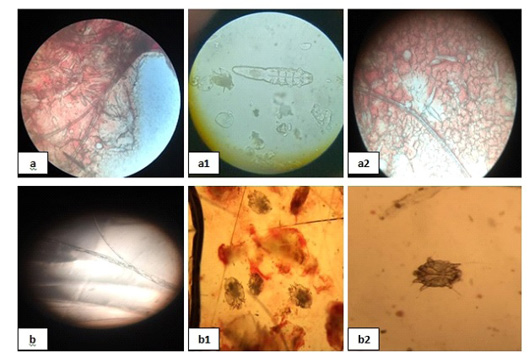
Mites and dermatophytes showing; 10 (a), (a1) and (a2) showed Demodex, (b) showed Microsporum and (b1), (b2) showed Sarcoptic mites.