Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
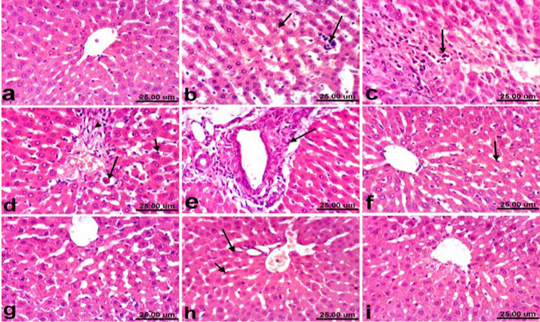
Liver of rat a) from control, normal group showing the normal histological structure of hepatic lobule from central vein surrounded by radiating hepatocytes. b), c), d) and e) treated with paracetamol, b) showing hepatocellular vacuolization (short arrow) and sinusoidal leukocytosis (long arrow). c) showing focal hepatocellular necrosis associated with inflammatory cells infiltration (arrow). d) showing Kupffer cells activation (short arrow) and apoptosis of hepatocytes (long arrow). e) portal fibrosis (arrow). f) co-treated with paracetamol + silymarin showing Kupffer cells activation (arrow). g) treated with silymarin showing no histopathological alterations. h). co-treated with paracetamol + cardamom showing slight activation of Kupffer cells (short arrow) and binucleation of hepatocytes (long arrow). i) treated with cardamom showing no histopathological alterations. (H & E, scale bar 25 um).
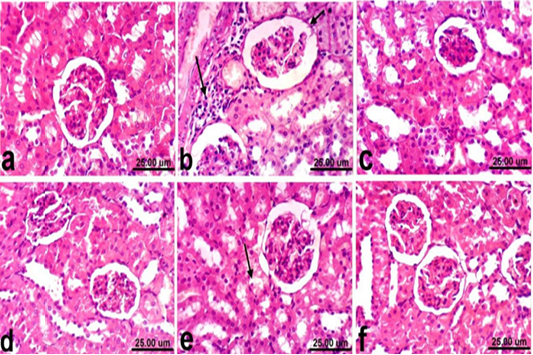
Kidney of rat a) from control, normal group showing the normal histological structure of renal parenchyma from renal cortex and medulla. b) Treated with paracetamol showing thickening of the parietal layer of Bowman’s capsule (short arrow) and focal inflammatory cells infiltration (long arrow). c) Co-treated with paracetamol+ silymarin showing apparent normal renal tissue. d) Treated with silymarin showing no histopathological alterations. e) co-treated with paracetamol + cardamom showing slight vacuolization of epithelial lining some renal tubules (arrow). f) Treated with cardamom showing no histopathological alterations. (H & E, scale bar 25 um).