Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
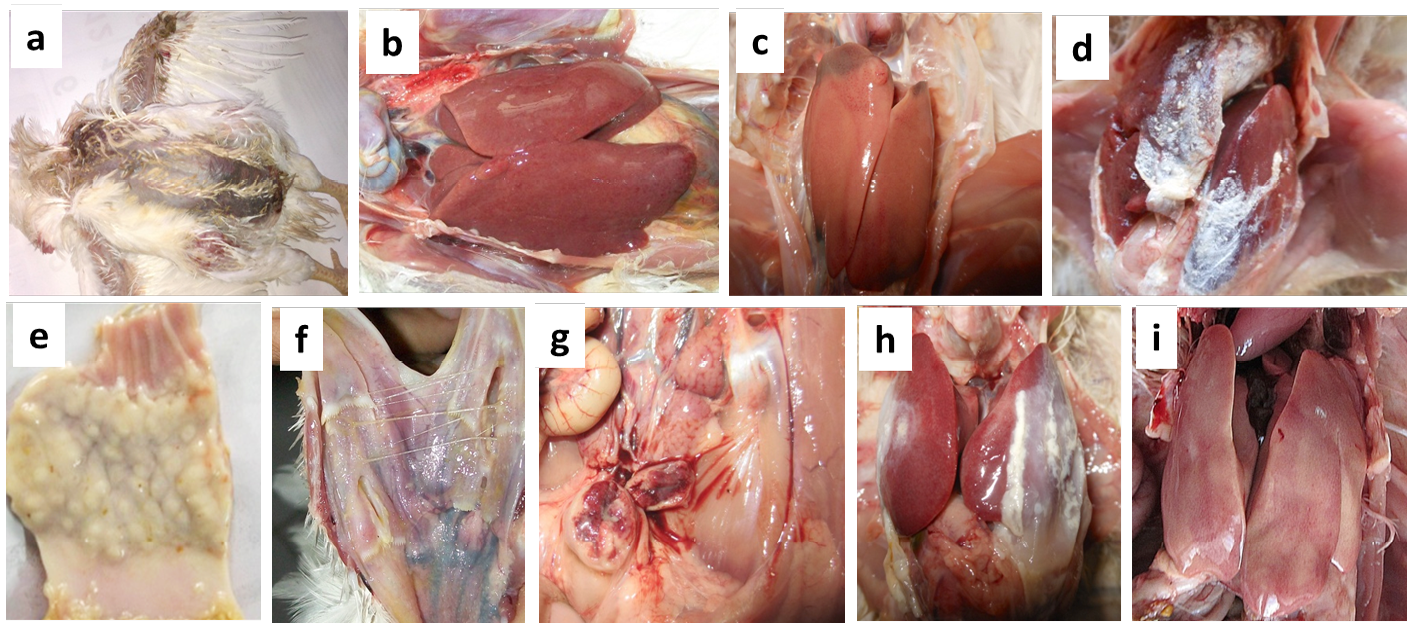
Necropsy findings of the suspected CAV infected poultry birds collected from different farms
(a) Moist haemorrhages on the skin of CIA-GDS affected bird;
(b) Nodular appearance of liver in Marek’s disease affected bird;
(c) Swollen liver with necrotic foci in CIA-GDS affected bird;
(d) Urate deposits in Gout affected bird;
(e) Thickened proventriculus in Marek’s disease affected bird;
(f) Caseous plug on opening of trachea in Fowl pox affected bird;
(g) Haemorrhages on mucosal surface of bursa in IBD affected bird;
(h) Pericarditis and perihepatitis in CCRD affected bird and
(i) Punctate haemorrhages on the liver of IBH affected bird
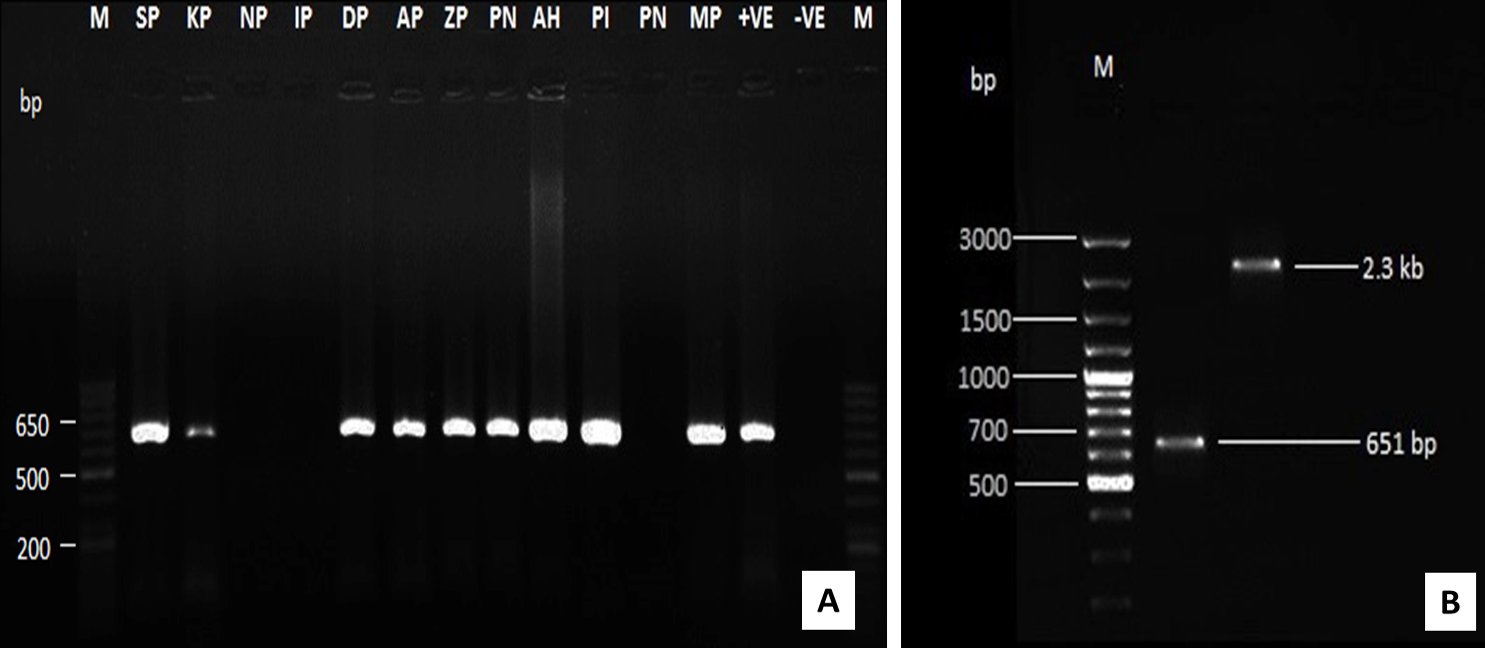
Amplification of CAV-DNA using PCR assay using VP2 specific primer (A) and by using both VP2 and full length genome primers (B)
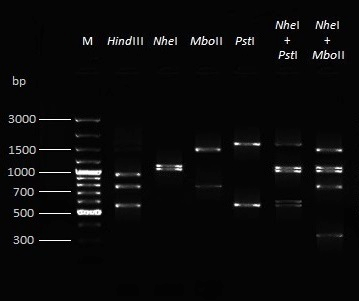
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) pattern after RE digestion of amplified full length CAV genome with four different enzymes and their combinations