Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
Ovicidal and larvicidal activities of Areca catechu crude aqueous extract (AAE).
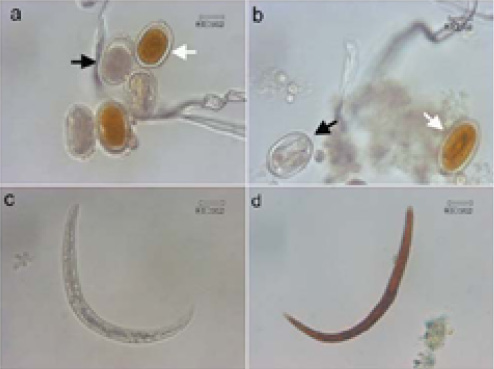
(a) The dead eggs (black arrow) and the surviving eggs (white arrow), (b) The dead eggs with hampered embryo formation (black arrow) and the eggs containing the surviving embryo (white arrow), (c) The dead larvae, (d) The surviving larvae.
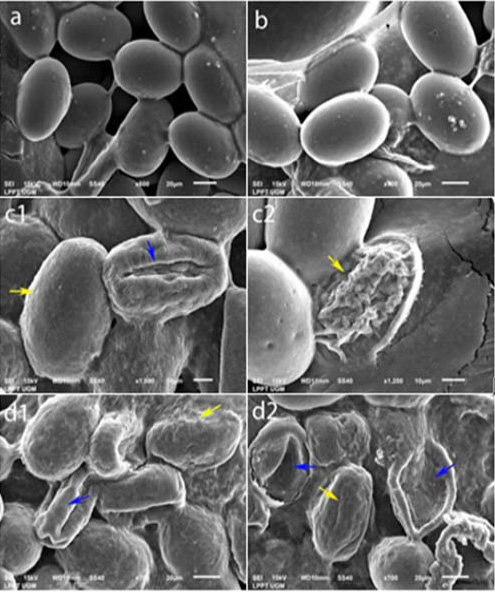
Egg ultrastructure ovicidal test results.
(a) Negative control. (b) 10% concentration: normal. (c1) 25% concentration: dotted egg wall surface (yellow arrow), shrinking egg wall (blue arrow). (c2) 25% concentration: ruptured egg wall (yellow arrow). (d1) Positive control: rough egg wall surface (yellow arrow), shrinking egg wall (blue arrow). (d2) Positive control: contracting egg wall (yellow arrows), ruptured egg wall losing its contents (blue arrow).
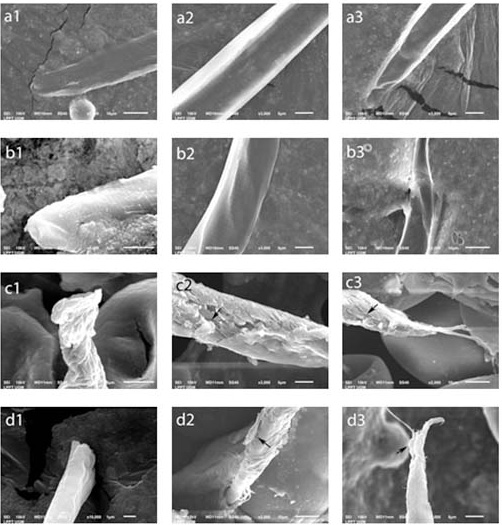
Larvae ultrastructure larvicidal test results.
(a) Negative control and (b) 10% concentration: normal. (c1) 25% concentration: the teguments of the anterior larvae shrink. (c2, c3) 25% concentration: the cuticle rupture/peel (arrow). (d1) Positive control: the anterior parts of the larvae begin to peel off. (d2, d3) Positive control: the cuticle rupture/peel (arrow).