Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
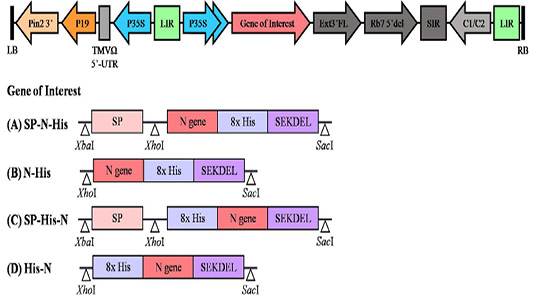
Schematic diagram of the plant expression vector used in the present study. LB and RB, the left and right borders of the gene region transferred by Agrobacterium into plant cells; Pin2 3′: the terminator from potato proteinase inhibitor II gene; P19: the RNA silencing suppressor from tomato bushy stunt virus; TMVΩ 5′-UTR: 5′ untranslated region of tobacco mosaic virus Ω; P35S: Cauliflower Mosaic Virus (CaMV) 35S promoter; LIR: long intergenic region of BeYDV; Gene of Interest: (A) SP-N-His, (B) N-His, (C) SP-His-N, (D) His-N; Ext3′FL: 3′ region of tobacco extension gene; Rb7 5′ del: tobacco RB7 promoter; SIR: short intergenic region of BeYDV; C1/C2: Bean Yellow Dwarf Virus (BeYDV) ORFs C1 and C2 encoding for replication initiation protein (Rep) and RepA.
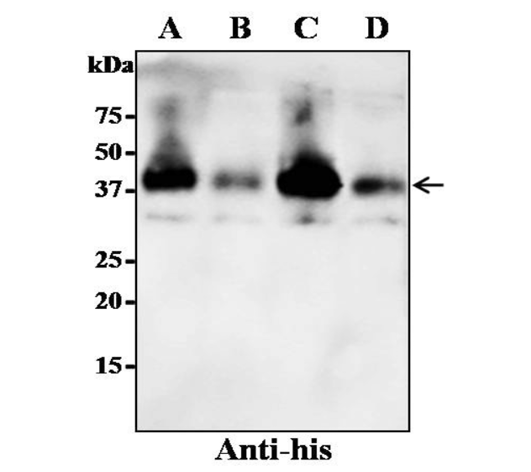
Expression of recombinant N-protein in N. benthamiana by using four different expression cassettes. The leaves were infiltrated with A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 containing either one of the four gene constructs. The crude proteins were extracted from the infiltrated leaves and the protein was separated on SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. The proteins on the blot were probed with a rabbit polyclonal anti-his antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. Lane A: SP-N-His; Lane B: N-His; Lane C: SP-His-N; Lane D: His-N. The arrowhead indicates the position of the recombinant protein.
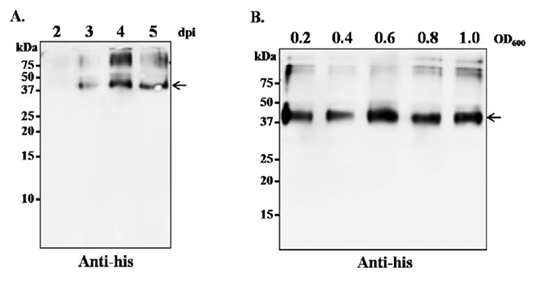
Optimization of leaf harvesting time and A. tumefaciens cell density for optimum transgene expression. (A) N. benthamaina leaves were infiltrated with A. tumefaciens containing plasmid pBYR2e-SP-His-N and the leaves were harvested on day 2, 3, 4 and 5 post infiltration. The protein was extracted from the infiltrated leaves and western blot was performed with rabbit polyclonal anti-His antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. (B) N. benthamaina leaves were infiltrated with A. tumefaciens containing plasmid pBYR2e-SP-His-N at OD600 of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8. The leaves were harvested 4 dpi and western blot was performed with rabbit polyclonal anti-his antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. The arrowhead indicates the position of the recombinant protein.
Western blot analysis of plant-produced recombinant N-protein detected with sera collected from pigs. The plant-produced N-protein was separated on SDS-PAGE gel and the proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. The blot (1-10) was incubated with panel of porcine sera at the dilution of 1:500 and then the bound antibody was detected with anti-porcine IgG antibody conjugated with HRP (1:5000). Commercial porcine anti-PRRSV serum was used as primary antibody in the positive control. The arrowhead indicates the position of the recombinant protein.