Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
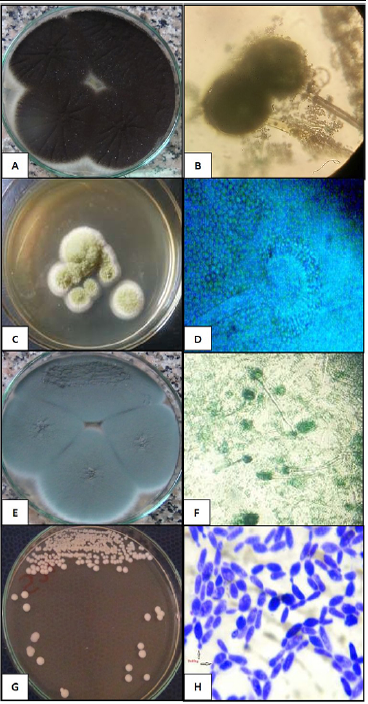
Colonial and microscopic characterization of the fungal and yeast isolates. (A and B) black dotted surface colonies of A. niger and septate hyphae, long conidiophores with large metulae and smaller phialides (40×). (C and D) A. flavus powdery yellow green colonies and microscopical globose vesicles producing phialides in two rows were observed (40×). (E and F) fluffy to granular white to blue green colonies of A. fumigatus colonies and septated hyphae, short conidiophores and bottle-shaped phialides (20×). The C. albicans creamy smooth glistening colonies and strong gram positive budding yeast cells (40×).
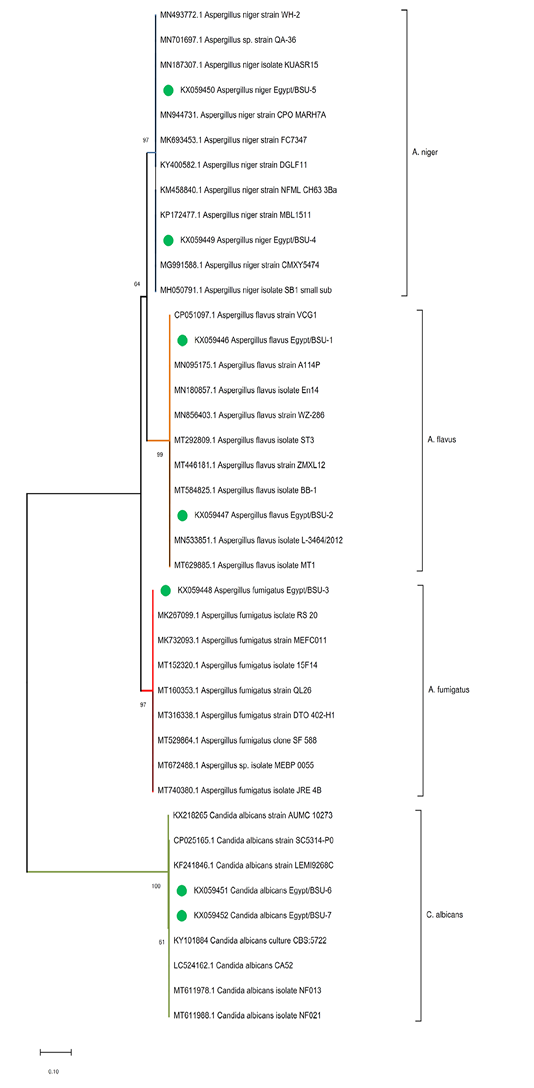
Phylogenetic tree of the ITS gene of the isolated fungi. The evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X and inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The analysis involved 41 nucleotide sequences with a total of 609 positions in the final dataset. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches.