Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
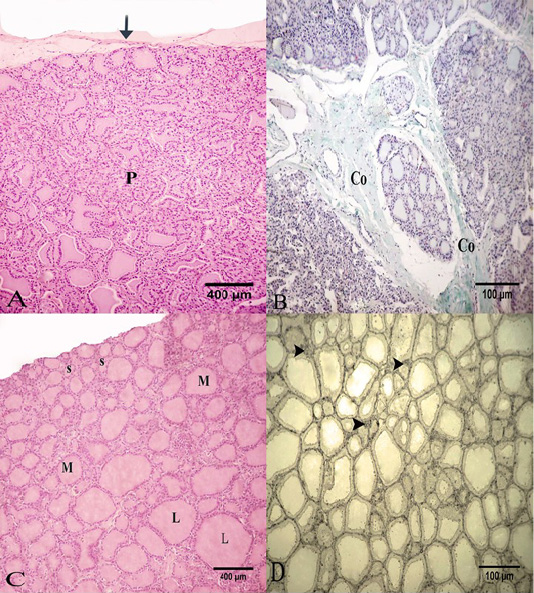
Photomicrograph of the goat’s thyroid gland showed that (A) Thyroid gland parenchyma “P” was surrounded by of a connective tissue capsule “arrow”. (B) Some connective tissue septa had mainly collagen fibers “Co”. (C) The parenchyma formed from several follicles; small “S”, medium “M” or large “L” in size. (D) The interfollicular connective tissue had little reticular fibers “arrow heads”. Stain: (A and C) H and E (B) Crossmon’strichrome (D) Silver impregnation (A and C) X.50, (B and D) X.100
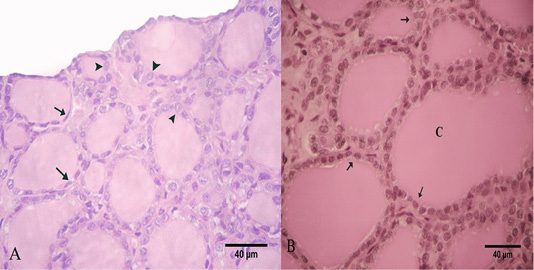
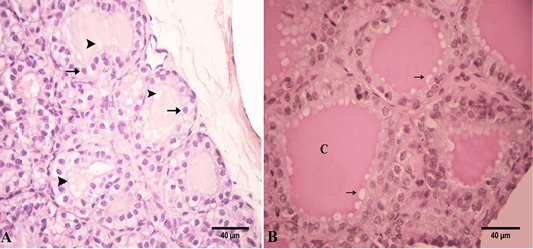
Photomicrograph of the goat’s thyroid gland showed that (A) In the summer season, most of the follicles were lined with simple squamous epithelium with flattened nuclei “arrows” and some follicles had low cuboidal epithelium “arrowheads”. (B) The follicles had a PAS-positive colloid “C” with smooth borders “arrows”. Stain: (A) H and E (B) PAS X.400.
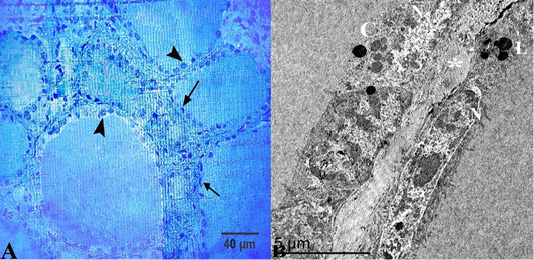
(A) Semithin section of thyroid gland in the summer season showed that thyroid follicles were lined with simple squamous epithelium with flattened nuclei “arrows” but some of them had low cuboidal epithelium “arrow heads”. (B) Ultrastructural characters showed that the thyroid follicles had flattened cells with an electron-dense cytoplasm and heterochromatic nuclei “N”, colloid droplets “C” and lysosomes “L”, these follicles were separated by interfollicular connective tissue “asterisk”. Stain:(A) Toluidine blue X.400.
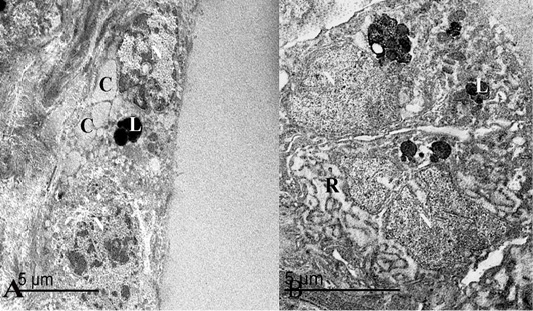
(A) An electron micrograph of thyroid gland in the summer season, showed that thyroid follicles were lined with flattened epithelium containing heterochromatic nuclei “N”, round lysosomes “L” and some colloid droplets “C”. (B) Follicular cells were low cuboidal in shape with heterochromatic nuclei “N”, lysosomes “L” and some rough endoplasmic reticulum “R”.
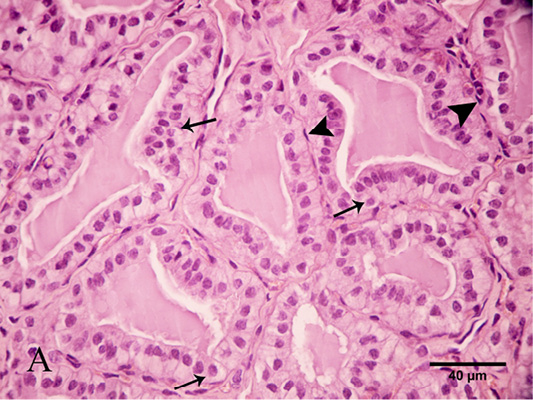
Photomicrograph of the goat’s thyroid gland showed that (A) In the winter season, thyroid follicles had high cuboidal epithelium with round nuclei “arrows”. These follicles had a vacuolated colloid “arrowheads”. (B) These follicles had a PAS-positive highly vacuolated “arrows” colloid “C”. Stain: (A) HandE (B) PAS X.400.
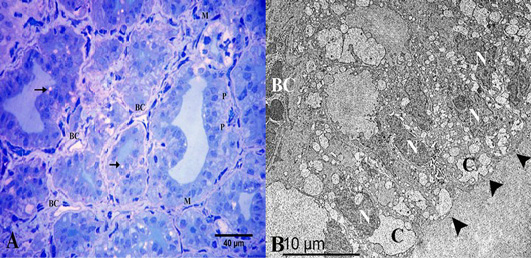
(A) Semithin section of thyroid gland in the winter season showed the thyroid follicles had high cuboidal epithelium, parafollicular cells in between “P” and vacuolated colloid “arrow”. They were surrounded by myoepithelial cells “M”. Note the thyroid follicles were surrounded by several blood capillaries “BC”. (B) Ultrastructural characters showed that the thyroid follicles had high columnar follicular cells “arrowheads” with heterochromatic nuclei “N” and several colloid droplets “C”. Note the blood capillary “BC”. Stain: (A) Toluidine blue X.400.
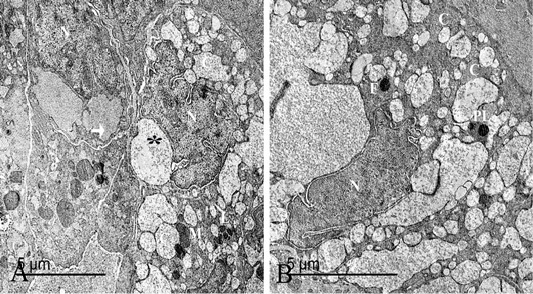
(A) An electron micrograph of thyroid gland in the winter season, showed synthetic subtype of the active follicular cells “arrow”, secretory subtype “star”, a compressed nucleus “N”, many colloid droplets “C”, numerous mitochondria “M” and lysosomes “L”. (B) The secretory follicular cell had a compressed nucleus “N”, many colloid droplets “C” and colloid filled endosomes fused “F” with the lysosomes forming phagolysosomes “PL”.
Photomicrograph of thyroid gland showed that parafollicular cells were seen between the follicular cells “arrows”. Note the thyroid follicles were surrounded by myoepithelial cells with flattened nuclei “arrow heads”. Stain: H and E X.400
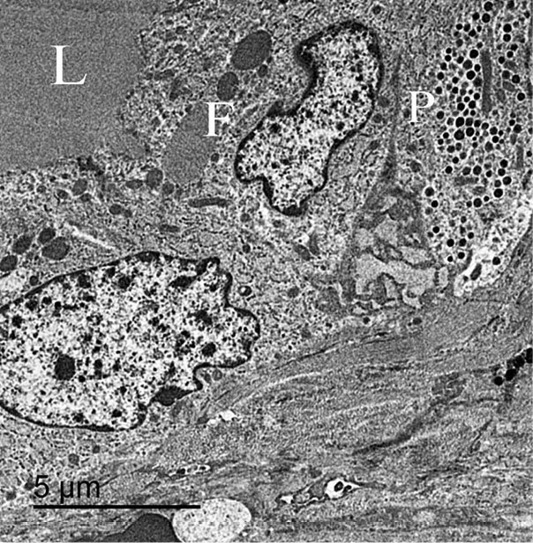
An electron micrograph of thyroid gland, showed that the parafollicular cells “P” present below follicular cells “F” and not reach the follicular lumen “L”.
An electron micrograph of thyroid gland, showed that parafollicular cells had large and central nuclei “N”, elongated mitochondria “M” and darkly stained granules “arrows”.