Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
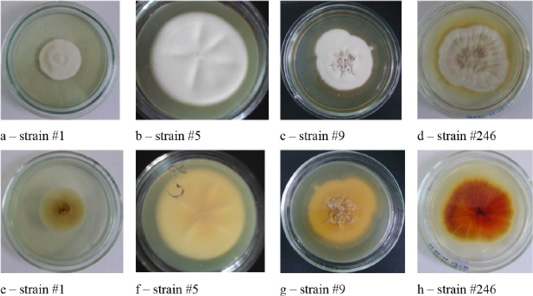
Colonies of isolates Trichophyton interdigitale. In the figure, letters a, b, c, and d show the front side, and letters e, f, g, and h show the reverse side of the colony.
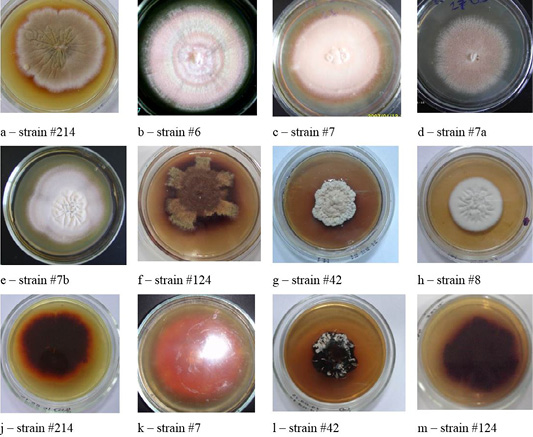
Colonies of clinical isolates of T. rubrum. Letters a, b, c, d, e, f, g, and h in the figure denote the front side, letters j, k, l, and m denote the reverse side of the colonies.
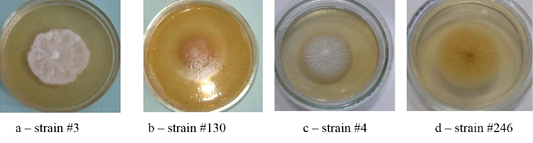
Clinical isolates of Trichophyton verrucosum from the front side of the colonies.
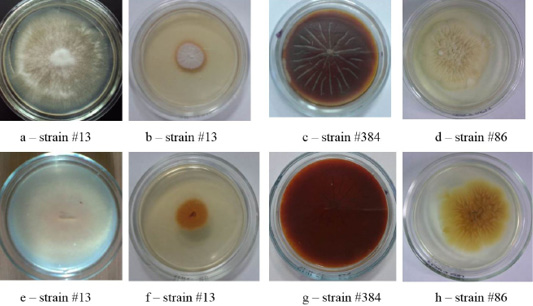
Clinical isolates of M. canis and T. tonsurans (strain #86). The Figure shows the front (a, b, c, d) and the reverse side of the colony (e, f, g, h).
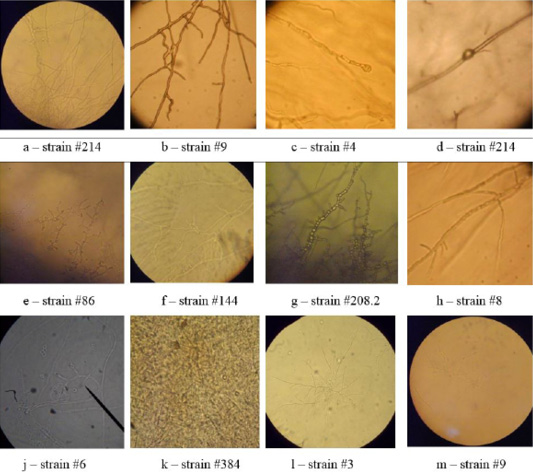
Morphological structure of dermatomycetes.
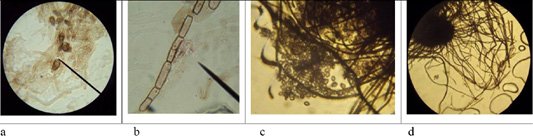
Morphological structures of microscopic fungi. Conidia (a) and mycelium (b) of micromycetes of Stemfyllium sp. #5.2; globular ascospores (c) and bristles (d) of Chaetomium globosum #129.