Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
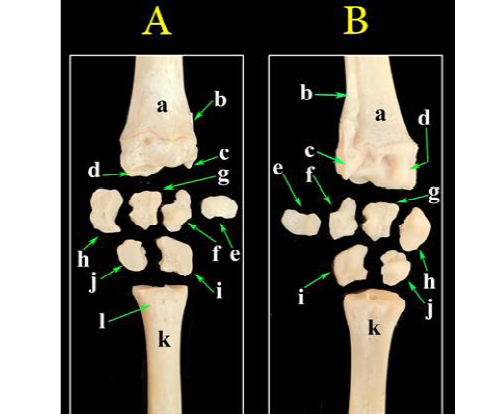
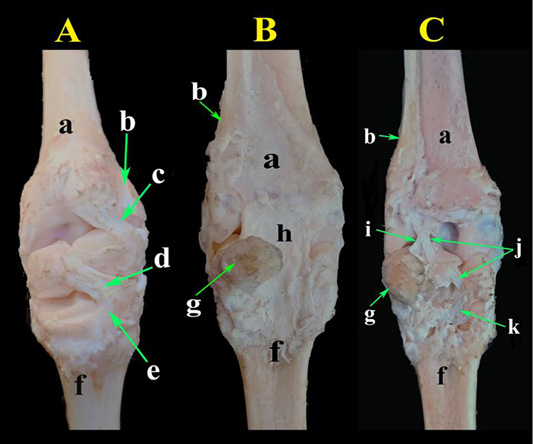
A photograph of bones of the carpal region. (A) Dorsal view, (B) palmar view. a- Radius; b- Ulna; c- Styloid process of ulna; d- Radial articular facets; e- Accessory carpal bone; f- Ulnar carpal bone; g- Intermediate carpal bone; h- Radial carpal bone; i- Fourth carpal bone; j- Fused second and third carpal bone; k- Metacarpal bones; l- Metacarpal tuberosity.
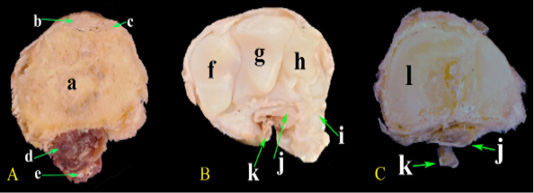
Photomacrograph of the cross sections at different levels of the carpal region. (A) At the distal extremity of radius, (B) At the middle carpal bones, (C) At the metacarpus. a-Radius; b- Extensor carpi radialis M.; c- Common digital extensor M.; d- Deep digital flexor M.; e- Superficial digital flexor M.; f- Radial carpal bone; g- Intermediate carpal bone; h- Ulnar carpal bone; i- Accessory carpal bone; j- Deep digital flexor tendon; k- Superficial digital flexor tendon; l- Metacarpal bones.
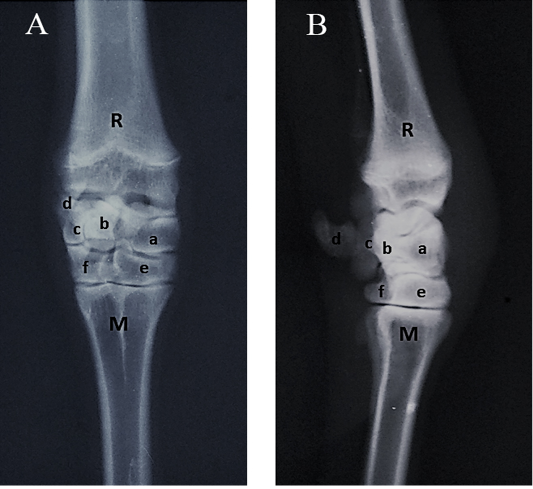
Radiographs of the carpal joint. (A) Dorsopalmar view, (B) Lateromedial view. R- Radius; M- Metacarpus; a- Radial carpal bone; b- Intermediate carpal bone; c- Ulnar carpal bone; d- Accessory carpal bone; e- Fused second, third carpal bone; f- Fourth carpal bone.
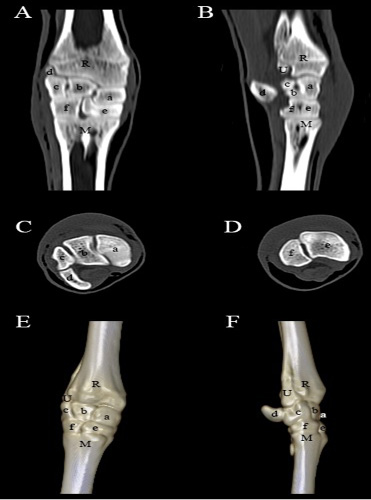
Computed tomography of the carpal joint. (A) Coronal view, (B) Sagittal scanning, (C) Axial scanning of the first raw of the carpal bones, (D) Axial scanning of the second raw of the carpal bones, (E) 3D image of the dorsopalmar aspect of the carpal joint, (F) 3D image of the lateromedial aspect of the carpal joint. R- Radius; U- Ulna; M- Metacarpus; a- Radial carpal bone; b- Intermediate carpal bone; c- Ulnar carpal bone; d- Accessory carpal bone; e- Fused second, third carpal bone; f- Fourth carpal bone.
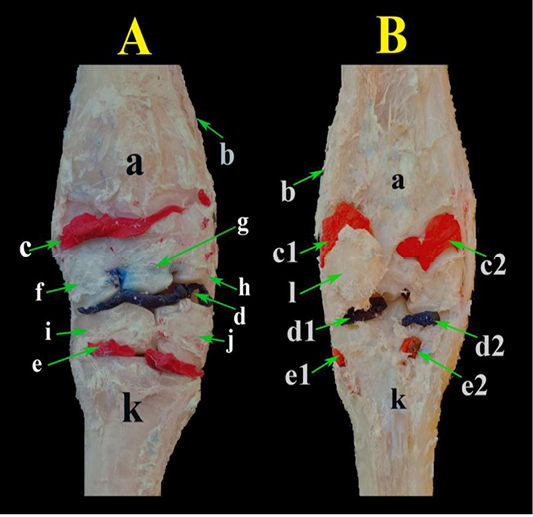
A photograph showing the carpal joint capsule injected with a colored latex. (A) dorsal view and (B) palmar view. a- Radius; b- Ulna; c- Antebrachial-carpal sac; c1- Lateral extension of antebrachial-carpal sac; c2- Medial extension of antebrachial-carpal sac; d- Middle carpal sac; d1- Lateral extention of of middle carpal sac; d2- Medial extension of of middle carpal sac; e- Carpometacarpal sac; e1- Lateral extension of of carpo-metacarpal sac; e2- Medial extension of of carpo-metacarpal sac; f- Radial carpal bone; g- Intermediate carpal bone; h- Ulnar carpal bone; i- Fused second, third carpal bone; j- Fourth carpal bone; k- Metacarpal bones; l- Accessory carpal bone.
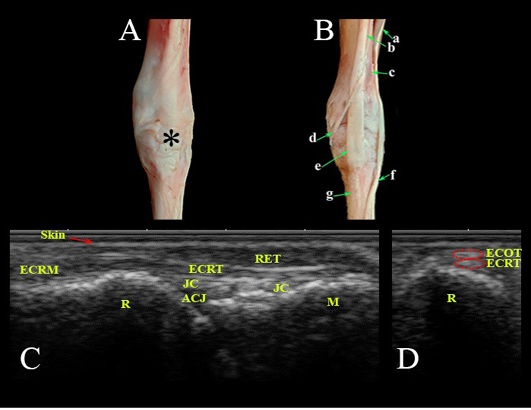
Dorsal aspect of the carpal region. Photomacrographs: (A) superficial layer and (B) deep layer. Ultrasonographic imaging: (C) Longitudianl scan (LS) and (D) Transverse scan (TS) at the level of the radius. *- Extensor retinaculum; a- Common digital extensor M.; b- Extensor carpi radialis M.; c- Extensor carpi obliqus M.; d- Tendon of extensor carpi obliqus M.; e- Tendon of extensor carpi radialis; f- Tendon of common digital extensor M.; g- Metacarpal bones; Ret- Retinaculum; ECRT- Extensor carpi radialis tendon; ECRM- Extensor carpi radialis M.; ECOT- Extensor carpi obliqus tendon; JC- Joint capsule; ACJ- Antebrachiocarpal joint; R- Radius; M- Metacarpus.
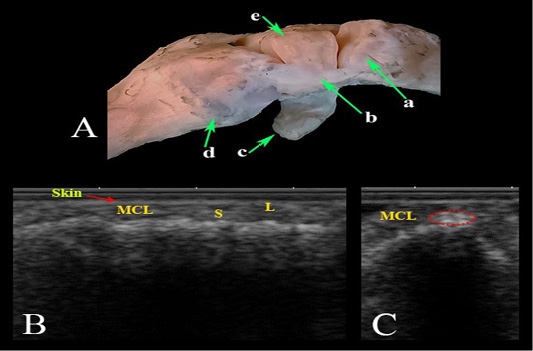
Medial collateral ligament of the carpal joint. (A) Photomacrograph. Ultrasonographic imaging: (B) LS, (C) TS. a- Radius; b- Medial collateral ligament; c- Accessory carpal bone; d- Metacarpal bones; (e) Radial carpal bone; MCL- Medial collateral ligament; L- Long fibers; S- Small fibers.
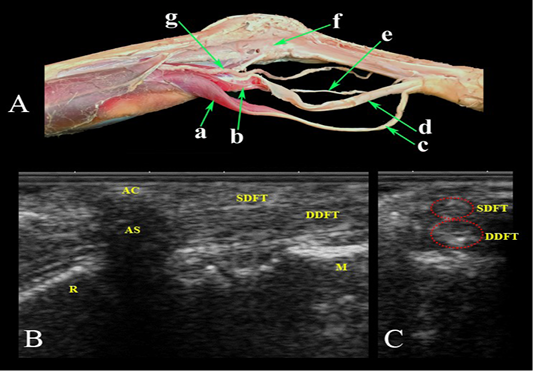
Palmar aspect of the carpal region. (A) Photomacrograph of the deep dissection of the forearm region and carpal canal. Ultrasonographic imaging: (B) LS and (C) TS. a- Superficial digital flexor M.; b- Deep digital flexor M.; c- Superficial digital flexor tendon; d- Deep digital flexor tendon; e- Median Nerve.; f- Carpal canal opened; g- Median Artery; AC- accessory carpal bone; AS- Acoustic shadow; SDFT- Superficial digital flexor tendon; DDFT- Deep digital flexor tendon; R- Radius; M- Metacarpus.
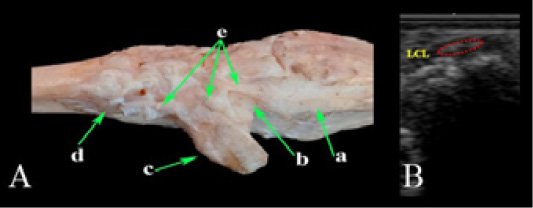
Lateral collateral ligament of the carpal joint. (A) Photomacrograph and (B) TS Ultrasonographic imaging. a- Ulna; b- Ulnar carpal bone; c- Accessory carpal bone; d- Metacarpal bones; e- Lateral collateral ligament; LCL- Lateral collateral ligament.
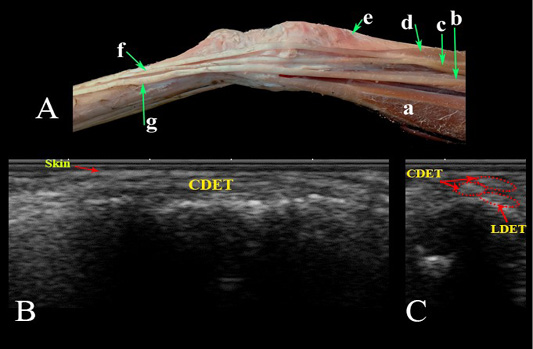
Lateral aspect of the carpal region. (A) Photomacrograph. Ultrasonographic imaging of the dorsolateral aspect of the carpal region: (B) LS and (C) TS. a- Ulnaris lateralis; b- Lateral digital extensor M.; c- Common digital extensor M. lateral belly; d- Common digital extensor M., medial belly; e- Extensor carpi obliqus M.; f- Tendon of common digital extensor; g- Tendon of lateral digital extensor M; LDET- Lateral digital extensor tendon; CDET- Common digital extensor tendon.
Photomacrographs of the special ligaments of the carpal joint. (A) Dorsal view, (B) Palmar view and (C) Palmar view after removal of the common palmar carpal ligament. a- Radius; b- Ulna; c- Dorsal radiocarpal ligament; d- Dorsal intercarpal ligament; e- Dorsal carpometacarpal ligament; f- Metacarpal bones; g- Accessory carpal bone; h- Common palmar carpal ligament; i- Palmar radiocarpal ligament; j- Palmar ulnocarpal ligament; k- Palmar carpometacarpal ligament.