Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
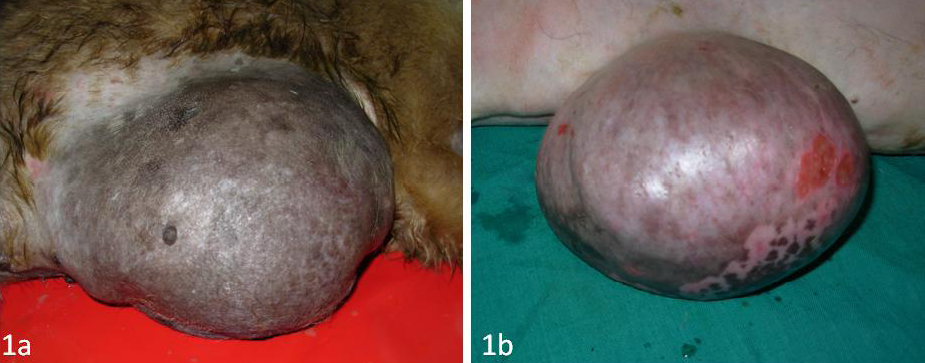
Mammary tumour in a female dog
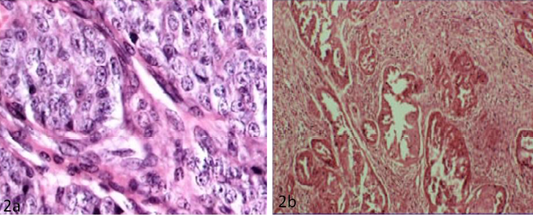
a) Solid carcinoma characterized by pleomorphic cells with vesicular nucleus (H&E x40); b) Papillary adenocarcinoma characterized by pockets of proliferative cells invading the parenchyma in papillary pattern with numerous mitotic figures (H&E x10)
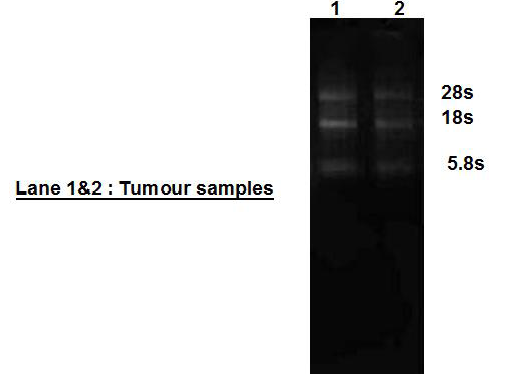
Quality and integrity of total RNase isolated from canine mammary tumour
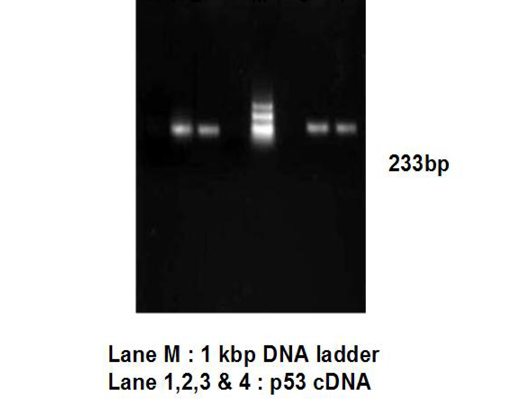
PCR amplification of cDNA to check DNA contamination
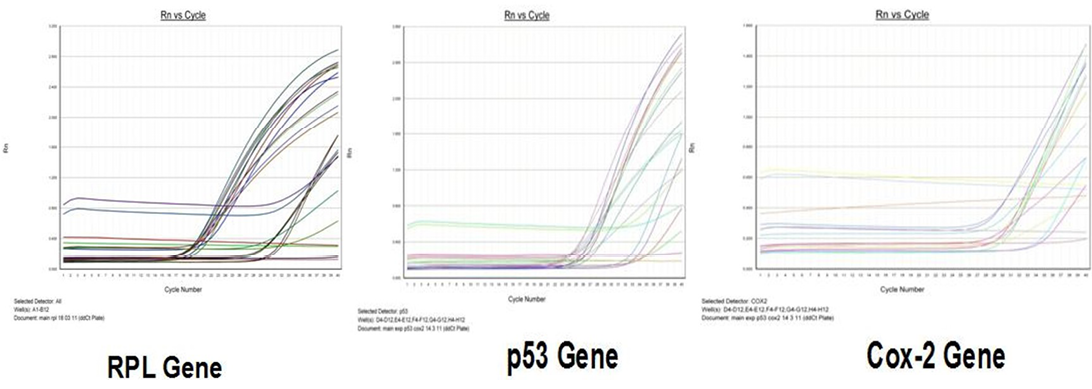
Amplification curve of different genes in RT-qPCR
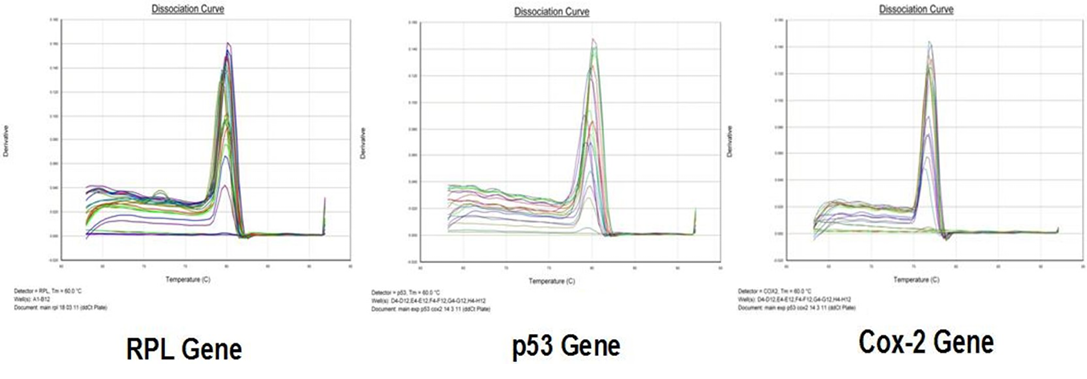
Dissociation curve of different genes in RT-qPCR
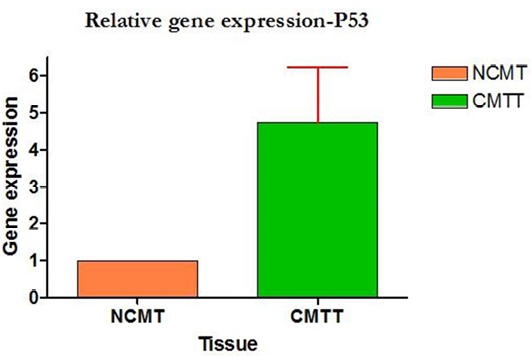
Relative gene expression of p53 gene (Group-wise)
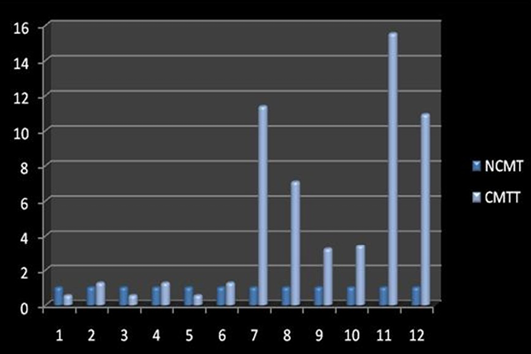
Relative gene expression of p53 gene (Individually) (NCMT-Normal canine mammary tissue; CMTT-canine mammary tumour tissue)
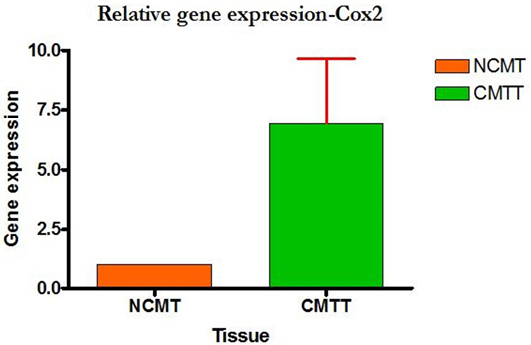
Relative gene expression of Cox-2 gene, (Group-wise)
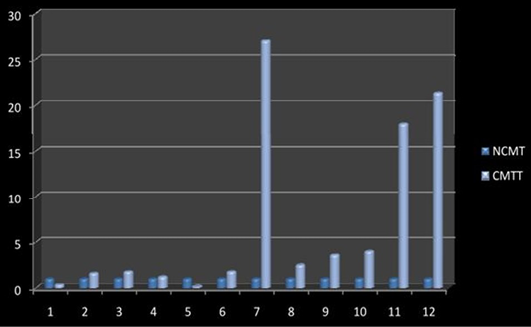
Relative gene expression of Cox-2 gene (Individually) (NCMT-Normal canine mammary tissue; CMTT-canine mammary tumour tissue)