Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
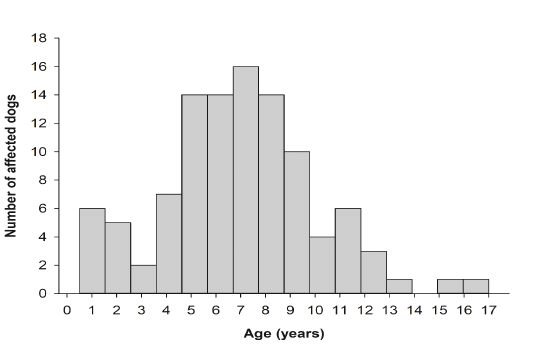
Number of dogs reported in the database in relation to age. More than half of the dog populations were between 5 and 9 years of age.
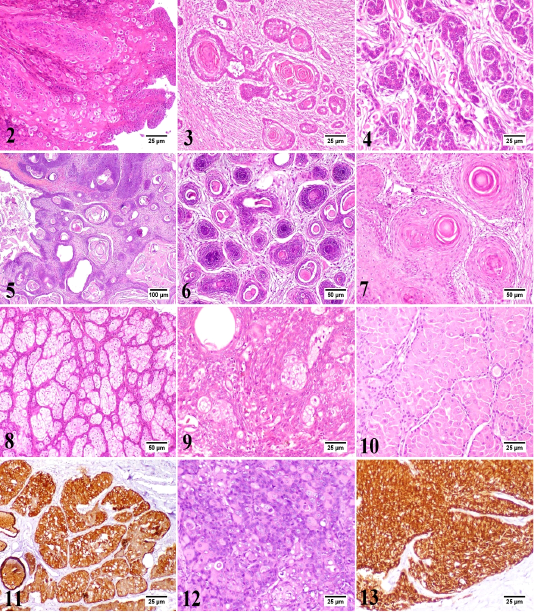
Canine papilloma, skin, dog. The hyperplastic epidermal cells are forming inward projections into the underlying stroma with marked parakeratosis. Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE). 3) Canine squamous cell carcinoma, skin, dog. The neoplasm is a well-differentiated. The neoplastic cells are forming a distinct keratin “pearls”. HE. 4) Canine basal cell carcinoma, skin, dog. Basophilic neoplastic cells with hyperchromatic nuclei are arranged in cords or sheets. HE. 5) Canine benign trichoepithelioma (Cystic variant), skin, dog. Multiple small cysts filled with keratinous debris. HE. 6) Canine malignant trichoepithelioma, skin, dog. The hyperchromatic neoplastic cells are invading into the dermis with central area of necrosis. HE. 7) Canine infundibular keratinizing acanthoma, skin, dog. Multiple cysts consisted of central lamellated keratin and proliferating keratinocytes were noticed. HE. 8) Canine sebaceous adenoma, skin, dog. The proliferating neoplastic cells are arranged in lobules separated by the pre-existing collagen of dermis. HE. 9) Canine sebaceous epithelioma, skin, dog. There are numerous small basophilic reserve cells with few sebocytes and ducts. HE. 10) Canine hepatoid gland adenoma, perianal gland, dog. The neoplastic cells are arranged in islands or trabeculae resembling the normal gland. HE. 11) Canine hepatoid gland adenoma, perianal gland, dog. Most neoplastic cells show intense immunolabelling. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for cytokeratin 14 (CK14). 12) Canine hepatoid gland adenocarcinoma, perianal gland, dog. Poorly differentiated neoplastic cells with hyperchromatic nuclei are arranged in clusters or irregular sheets. HE. 13) Canine hepatoid gland adenocarcinoma, perianal gland, dog. The neoplastic cells show intense immunolabelling. IHC for CK14.
Canine meibomian adenocarcinoma, meibomian gland, dog. The neoplastic cells are grouped in lobules with presence of intracytoplasmic lipid vacuoles of variable sizes. HE. 15) Canine apocrine gland adenoma, skin, dog. The gland is lined by simple cuboidal cells with secretory blebs on the luminal surface. HE. 16) Canine ceruminous gland adenoma, skin, dog. The tumor resembles the normal gland with retention of intraluminal material. HE. 17) Canine ceruminous gland carcinoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells are arranged in clusters with marked pleomorphism. HE. 18) Canine melanocytoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic melanocytes are present at the lower layers of the epidermis and just beneath the epidermis either as single cells or as small clusters. HE. 19) Canine malignant melanoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells are showing variable intracytoplasmic content of melanin pigment infiltrating the superficial dermis. HE. 20) Canine lipoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells are vacuolated, variable sized and are arranged in lobules with fine fibrous separating septa. HE. 21) Canine fibroma, skin, dog. The tumor is consisted of interwoven bundles of collagen. HE. 22) Canine liposarcoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells have variable sized fat vacuoles with marked pleomorphism. HE. 23) Canine fibrosarcoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells are pleomorphic and forming interlacing fascicles with little deposition of collagenous matrix. HE. 24) Canine fibrosarcoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells show intense immunolabelling. IHC for vimentin. 25) Canine myosarcoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic stellate and spindle-shaped cells are suspended in faint blue myxomatous matrix. HE.
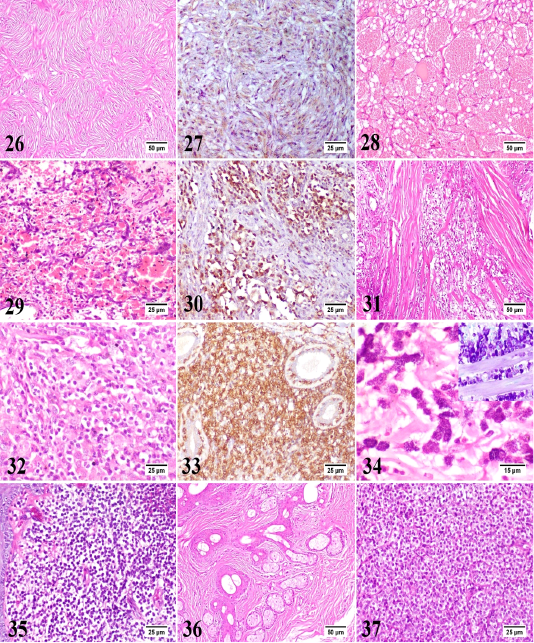
Canine peripheral nerve sheath tumor, skin, dog. The spindle neoplastic cells are arranged in wavy bundles, palisades and whorls. HE. 27) Canine peripheral nerve sheath tumor, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells show moderate immunolabelling. IHC for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). 28) Canine hemangioma, skin, dog. The tumor is formed of variably sized blood spaces containing erythrocytes and lined by a single layer of uniform endothelial cells. HE. 29) Canine hemangiosarcoma, skin, dog. The plump neoplastic endothelial cells are forming irregular blood spaces and filling the trabeculae in between. HE. 30) Canine hemangiosarcoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells show intense immunolabelling. IHC for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). 31) Canine rhabdomyosarcoma, skin, dog. The neoplasm is formed of numerous pleomorphic neoplastic cells with frequent atypical mitosis and few skeletal muscle bundles. HE. 32) Canine epitheliotropic lymphoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic T-cells are infiltrating the dermis with increased affinity for epidermis and adnexal epithelium. HE. 33) Canine epitheliotropic lymphoma, skin, dog. The neoplastic cells show intense immunolabelling. IHC for CD3. 34) Canine mast cell tumor, skin, dog. The neoplastic mast cells are round, monomorphic with abundant basophilic granules. HE. Inset: Canine mast cell tumor, skin, dog. The metachromatic granules of mast cells are dispersed in the cytoplasm. Toluidine blue. 35) Canine cutaneous histiocytoma, skin, dog. The dermis is densely packed by slightly pleomorphic cells with little or no stroma. HE.
36) Canine sebaceous hamartoma, skin, dog. Proliferating mature sebaceous glands are found in the mid dermis with marked peri-glandular fibrous tissue proliferation. HE. 37) Canine transmissible venereal tumor, skin, dog. The neoplasm is formed of uniform round cells with vacuolated cytoplasm as well as frequent mitotic figures and scanty stroma. HE.