Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
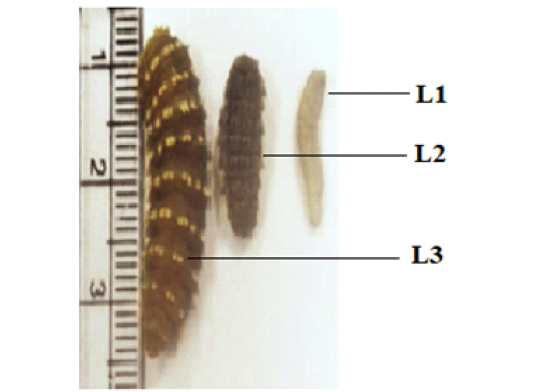
The three phases of instars larvae of C. titillator from infested camels
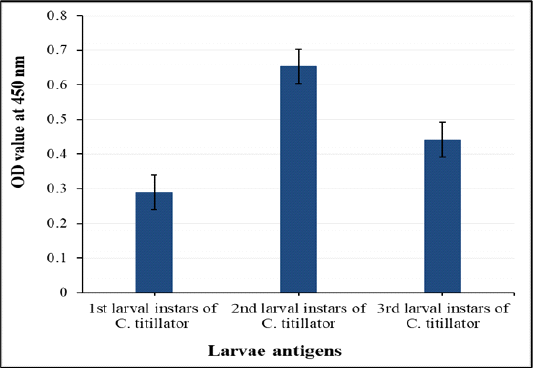
Comparative diagnostic potency of three crude first, second and third antigens in detection of anti- C. titillator IgG in naturally infested camels’ sera
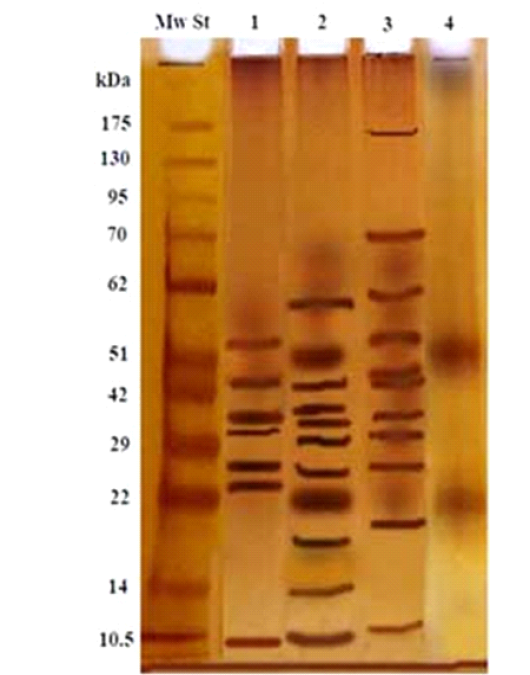
Electrophoretic profile of the isolated 2nd larval fraction (Lane 4), and crude first larvae (Lane 1), crude second larvae (Lane 2), crude third larvae (Lane 3) and Molecular weight standards (Lane Mw St).
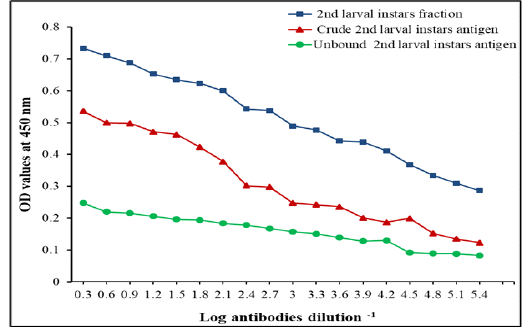
IgG Level measured by ELISA with specific fraction, its crude 2nd larvae and unbound antigens in detection of IgG in camels’ sera naturally infested by C. titillator larvae
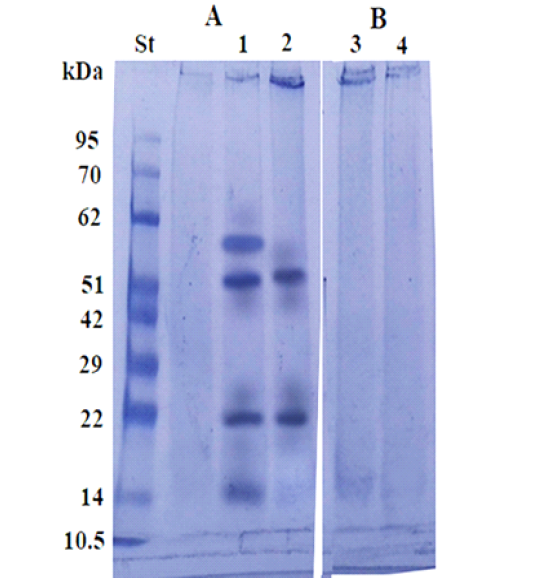
Immunoblot analysis of the larval purified fraction (2, 4) and its crude extract (1, 3), using pooled sera of infested (A) and non-infested camel sera by Cephalopina nasal myiasis (B).
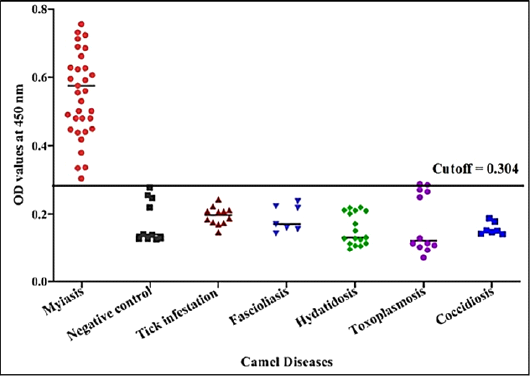
Detection of specific C. titillator antibodies IgG in positive camel sera and different sera of camel diseases using larval fraction by ELISA
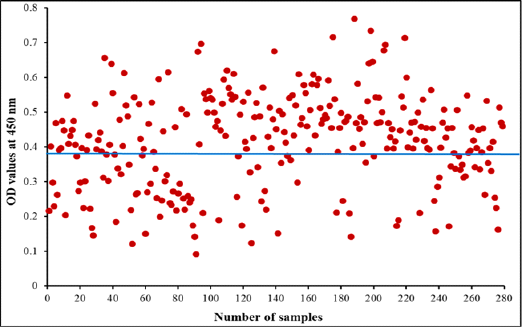
Diagnostic potency of purified fraction for camel Cephalopina nasal myiasis by indirect ELISA. The blue line represents cut off at 0.390 in collected random samples