Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
Examination sheet.
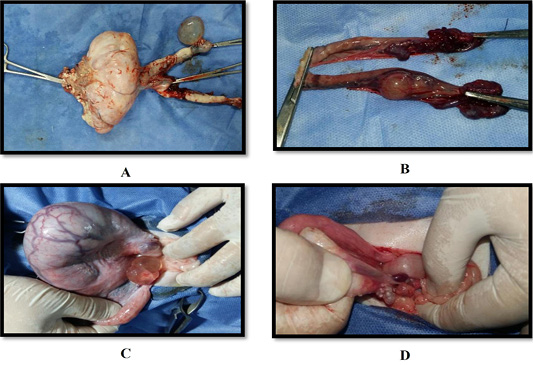
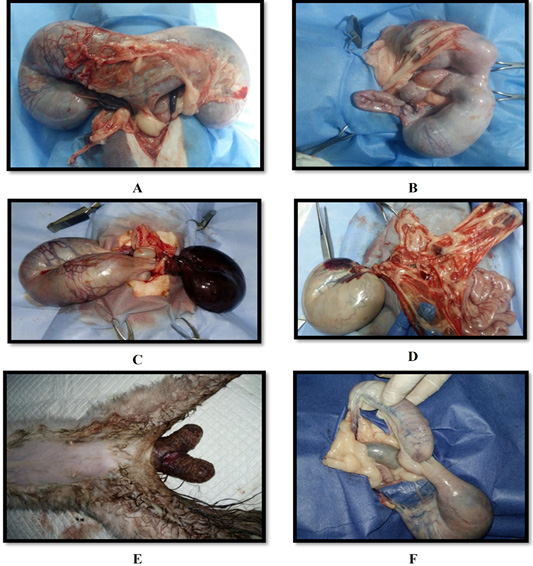
(A) Ovary of queen 12 years old suffered from cyst and large mass; (B) Ovary of queen 11 years old suffered from mass; (C) Ovary of queen 7 years old suffered from cyst; (D) Ovary of queen 5 years old suffered from many cyst.
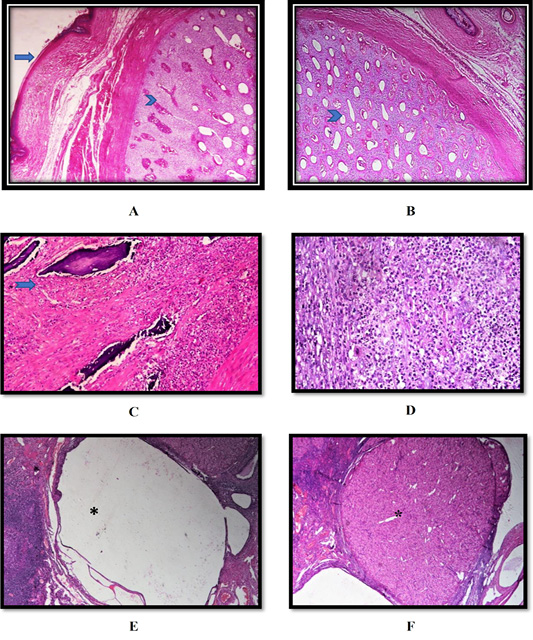
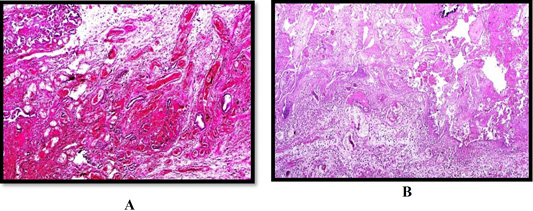
(A, B) Ovary of queen showing Ovarian in teratoma in which had well developed cartilage (arrowhead), and skin (arrow) (H and E stain 40); (C, D) Ovary of queen showing Severe neutrophilic in the interstitial which focal areas of liquefactive necrosis and calcification (suppurative oophoritis) (arrow) (H and E stain left X 200, right X400); (E, F) Ovary of queen showing follicular cyst (asterisk) (left) and luteal cyst (asterisk) (right) (H and E stain X100).
(A) Radiograph for pyometra in queen showing a sausage-like fluid filled tubular organ; (B) B- mode ultrasound sagittal scan at the level of right flank region of a 3- years- old Persian cat suffered from closed pyometra. Notice hyperechoic thickened wall with intralumenal trapiculi and anechoic content of the right uterine horn.
(A) Uterus of Persian queen 5 years old showing closed pyometra; (B) Uterus of mixed breed queen 8 years old showing closed pyometra; (C) Uterus of Persian queen 3 years old showing open pyometra; (D) Uterus of Persian queen 2 years old showing closed pyometra.
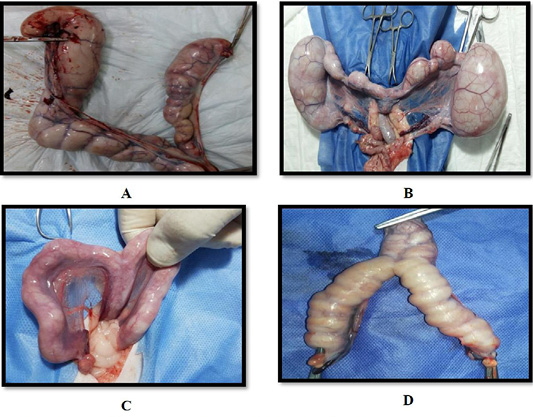
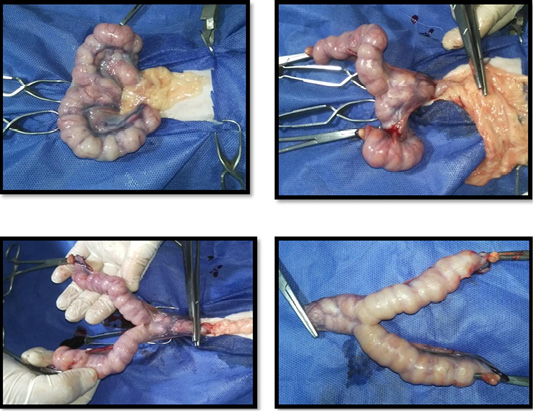
(A) Uterus of Persian queen 4 years old suffered from dystocia and subjected to OHE, note: presence of uterine adhesion at the level of uterine bifurcation; (B) Uterus of Persian queen 2 years old suffered from dystocia and subjected to OHE, note: presence of uterine adhesion at the level of right uterine horn; (C) Uterus of Persian queen 5 years old showing left uterine horn torsion, note: the torsion was at two levels, the first at the level of left ovary and the second at the level of uterine bifurcation; (D) Uterus of Persian queen 2 years old showing right uterine horn torsion, note: the torsion was at two levels, the first at the level of right uterine and the twisted part contained retained fetus; (E) Uterus of Persian queen one and half years old showing complete uterine prolapse; (F) Uterus of Persian queen 2 years old showing left uterine horn prolapse, note: the right uterine horn contained retained fetus.
(A) Uterus of queen showing congestion, endema, hemorrhage, necrosis and few inflammatory cells infiltration in the endometrium (Uterine prolapse) (H and E stain X 100); (B) Uterus of queen showing endometrial necrosis and leukocytic infiltration in the case of Uterine torsion (H and E stain X 100).
Pathological OHE in 5-years old mix breed queen suffered from open pyometra.
Pathological OHE in 4-years old mix breed queen suffered from uterine prolape.
Caesarian in mixed breed queen two years old.
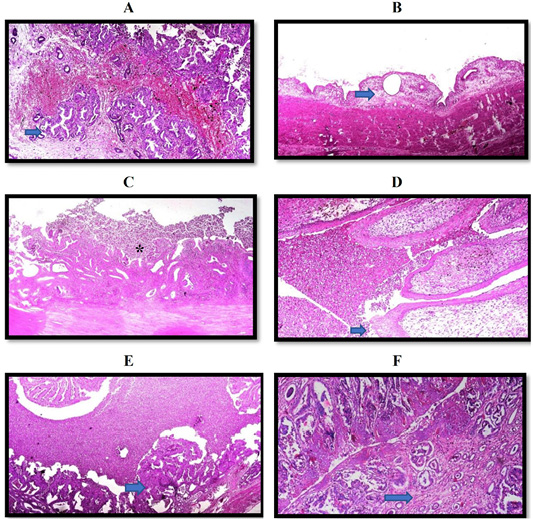
(A) Uterus of queen showing hemorrhage and Endometroid intraepithelial neoplasia Adenocarcinoma (arrow) (H and E stain X 100); (B) Uterus of queen showing Cystic endometrial hyperplasia (arrow) (H and E stain X 40); (C) Uterus of queen showing Cystic endometrial hyperplasia and pyometra. The uterine lumen is dilated and filled with neutrophils and necrotic debris (asterisk). The myometrium is thin and stretched. Some of the endometrial stroma contains mostly mononuclear cells (H and E stain X 40); (D) Cervix of queen showing papillomatosis, cytoplasmic clearing [Halos) of the epithelium (arrow) and necrotic debris and neutrophils in the lumen (H and E stain X 200); (E) Uterus of queen showing Cystic endometrial hyperplasia and pyometra in which the lumen is filled with neutrophils and necrotic (arrow) (H and E stain X 100); (F) Uterus of queen showing leukocytic infiltration in the endometrium which characterizes endometritis and mild peri-glandular fibrosis (arrow) (H and E stain X 100).
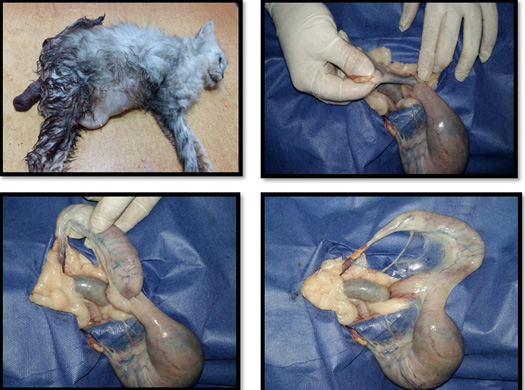
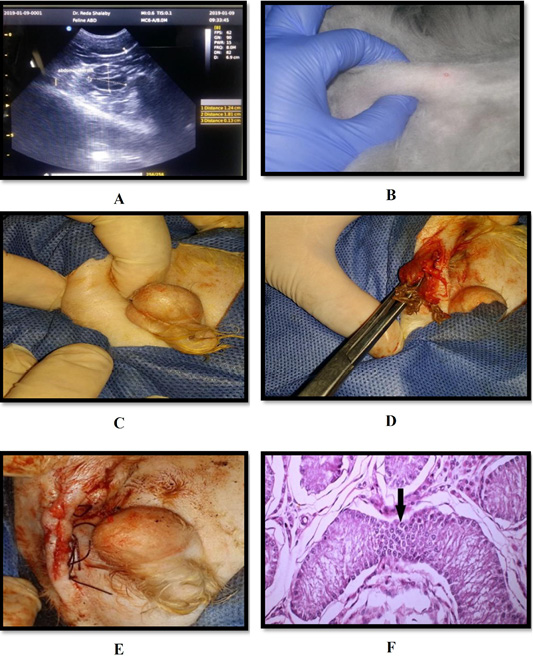
(A) B-mode sagittal scan in an 8 months old Persian tomcat suffered from unilateral ectopic testis. Notice the homogenous hypoechoic testis with hyperechoic reta testi and testicular capsule. The size of the affected testis was 1.8×0.9 cm; (B) Abdominal tests; (C) Ectopic testis; (D, E) Cryptorchidectomy; (F) Seminiferous tubules showing proliferation in Sertoli cells (Sertoli cell tumor) (arrow) (H & E×200).