Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
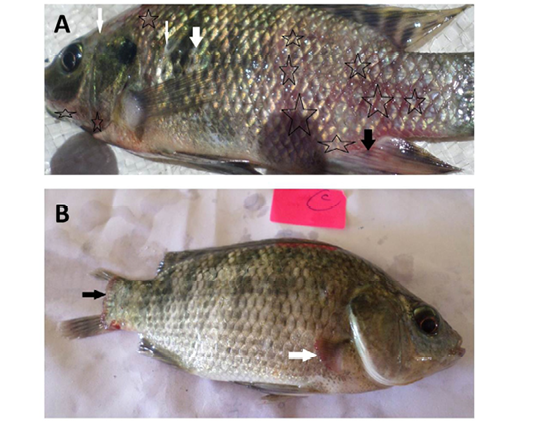
Oreochromis niloticus naturally infected with bacterial pathogens showing:
A: Hemorrhages all over the body (stars) especially on anal fin (black arrow) and detachment of scales (white arrows).
B: Caudal fin erosion (black arrow) and pectoral fin erosion (white arrow).
Oreochromis niloticus naturally infected with bacterial pathogens showing:
A: Hemorrhages all over the body (stars), detachment of scales (white arrow) and cloudy eye (black arrow).
B: Hemorrhages arround the mouth (white arrow), detachment of scales (stars) and erosion of pectoral fin (black arrow).
C: Hemorrhages all over the body (stars) and cloudy eye (black arrow).
D: Distended gall bladder (black arrow) and pale liver (star).
Oreochromis niloticus naturally infected with bacterial pathogens showing:
A: Sanguineous ascitic fluid in the abdominal cavity (arrows), pale enlarged liver (stars) and marbling (mosaic) appearance of the gills.
B: Gaseous intestinal content and marbling (mosaic) appearance of the gills with excessive mucus secretions.
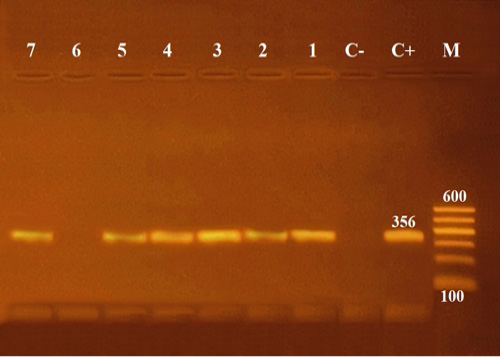
Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR of 16S rRNA (356 bp) as species specific gene for confirmation of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Oreochromis niloticus.
Lane M: 100 bp ladder as molecular size DNA marker.
Lane C+: Control positive Aeromonas hydrophila for16S rRNA gene.
Lane C-: Control negative.
Lanes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 & 7: Positive Aeromonas hydrophila strains.
Lane 6: Negative Aeromonas hydrophila.
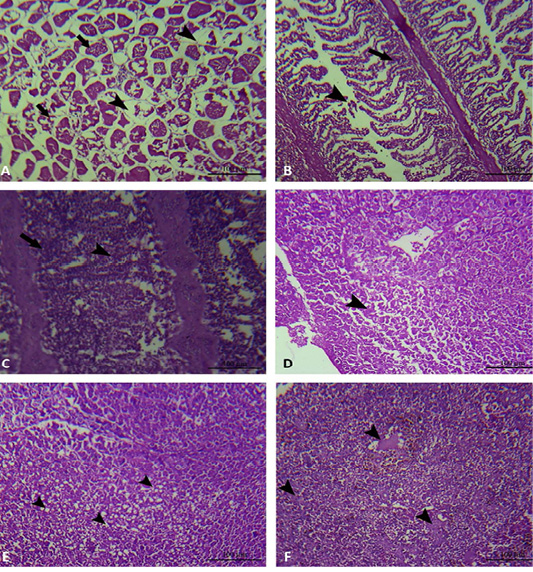
Muscle, gills and liver of experimentally infected Oreochromis niloticus with Aeromonas hydrophila. A: The muscular tissue showing interstitial edema (black arrow head), degeneration and loss of muscle architecture (black arrow). B and C: The gills showing mononuclear cell infiltration (black arrow), in addition to epithelial lifting and loss of secondary lamellae (black arrow head). D: The hepatic tissue showing degeneration and loss of hepatocellular architecture (black arrow head). E: The hepatic tissue showing hepatocellular vacuolation (black arrow head). F: The hepatic tissue showing hepatocellular necrosis (black arrow head).