Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
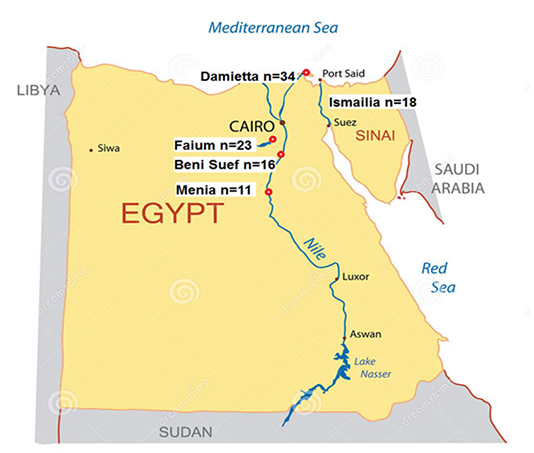
Areas of study and number of examined animals
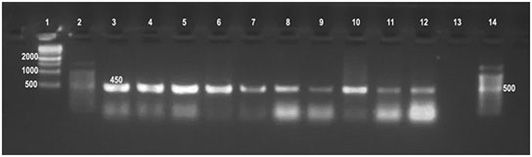
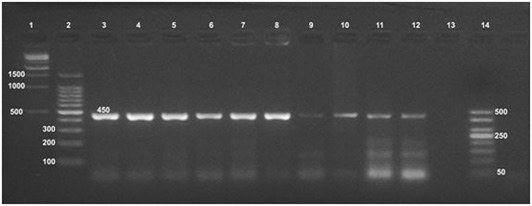
Detection of Brucella in culture and tissue using universal PCR assay.
Detection of Brucella organisms in culture, fresh tissue and in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues by Universal PCR
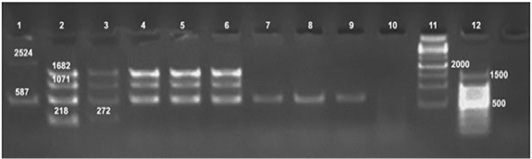
Detection of Brucella organisms in culture, fresh tissue and in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues by Bruce-ladder PCR
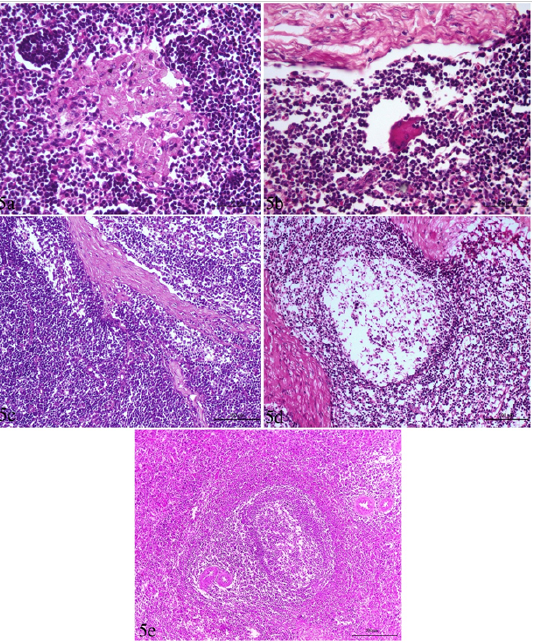
Lymph node and spleen of brucellosis-positive cows exhibiting (a) Epithelioid cell reaction. (b) Giant cell reaction. (c) Mononuclear cells accumulation in trabecular sinuses (sinus catarrh). (d) Depletion of lymphocytes in the white pulp of spleen and cortex of a lymph node. (e) Hyperplasia of white pulp in the spleen (e).
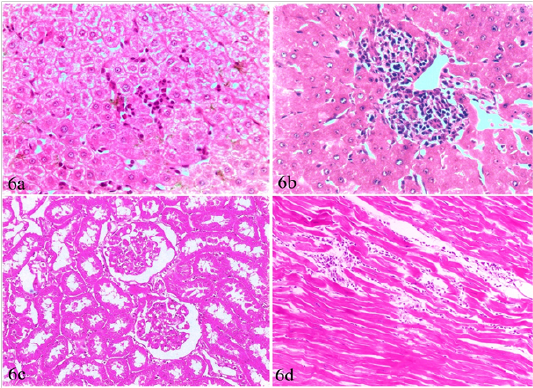
Liver, kidney and heart of brucellosis-positive cows showing (a) Active proliferation of Van Kupffer cells. (b) Mononuclear cells infiltration in hepatic parenchyma. (c) A kidney showing glomerular and tubular nephrosis. (d) A heart suffered from myocarditis and necrotic changes.
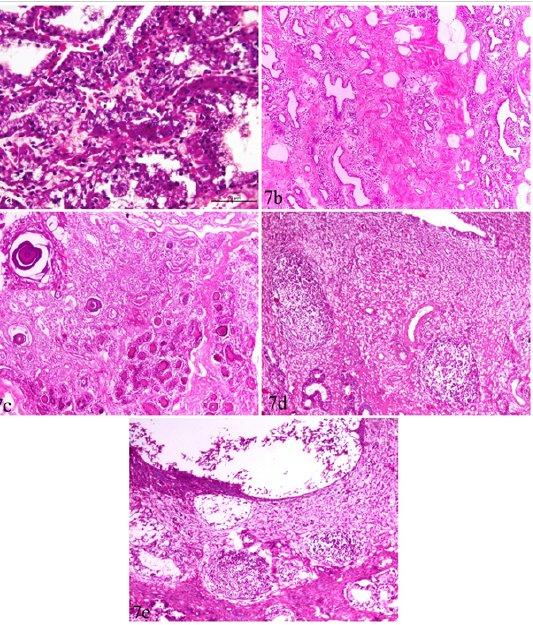
Udder and uterus of brucellosis-positive cows showing (a) Acute catarrhal mastitis. (b) Chronic interstitial mastitis. (c) Bluish-red bodies (corpora amylacia) occupying acini of chronically infected udder. Inset in a higher magnification. (d) Moderate endometritis with focal leucocytic infiltration. (e) Endometritis with severely detached epithelial surface.