Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
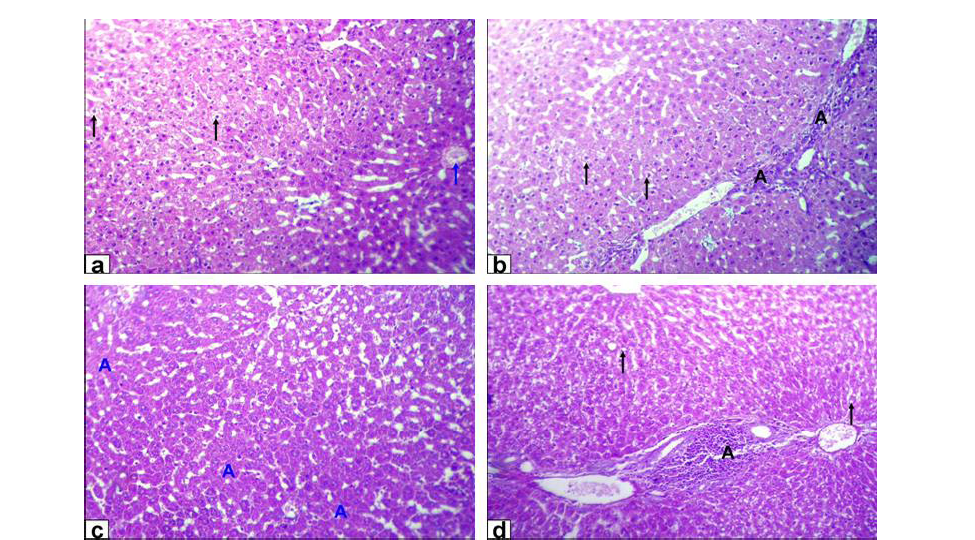
Photomicrographs of liver sections stained with HE from: a and b) Rats treated with low dose of Lead acetate (1g/L) showing hydropic degeneration of the hepatocytes (black arrows), congestion of central vein (blue arrow), loss of cord arrangement of hepatocytes and portal tract with few aggregation of mononuclear inflammatory cells (black A X200); c and d) Rats treated with high dose of Lead acetate (2g/L) showing hepatocytes focal necrosis (blue A) beside fatty degeneration (black arrows) and portal tract with massive aggregation of mononuclear inflammatory cells which scattered in different spaces (black A) with biliary hyperplasia (X200)
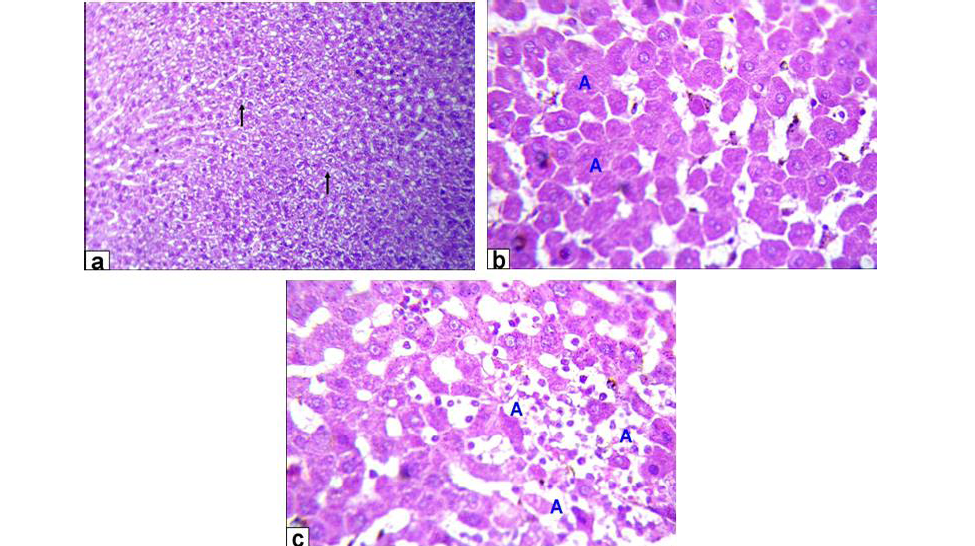
Photomicrographs of liver sections stained with HE from: a) Rats treated with low dose of Aluminium chloride (2g/L) showing moderate hydropic degeneration of the hepatocytes (arrows X200); b and c) Rats treated with high dose of Aluminium chloride (3.5g/L) showing hepatocytes necrosis with nuclei was fragmented, ghost or pyknotic and finally necrotic hepatocytes infiltrated with inflammatory cell (blue A, X 400)
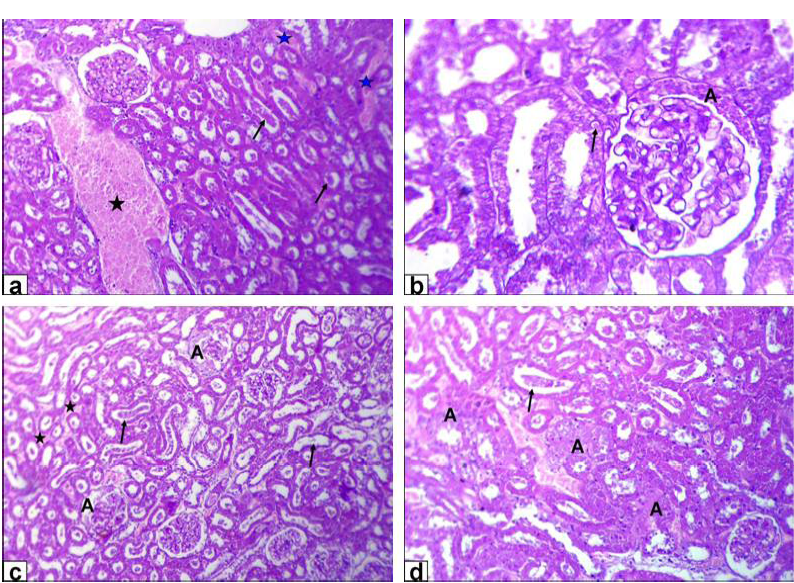
Photomicrographs of kidney sections stained with HE from: a and b) Rats treated with low dose of Lead acetate (1g/L) showing congestion of the blood vessel (black star) and inter-tubular blood capillaries (blue stars), cellular debris in the lumen of the renal tubules (arrows, X200) beside eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions in lining epithelium of renal tubules and glomerulus’s filtrate occupied the space of bowman capsule (black A, X400); c and d) Rats treated with high dose of Lead acetate (2g/L) showing tubular dilatation (arrows), haemorrhage (stars) and glomerulus’s filtrate occupied the space of bowman capsule (A, X200) in addition tubular necrosis (A) and cellular debris in the lumen of the renal tubules (arrow, X200)
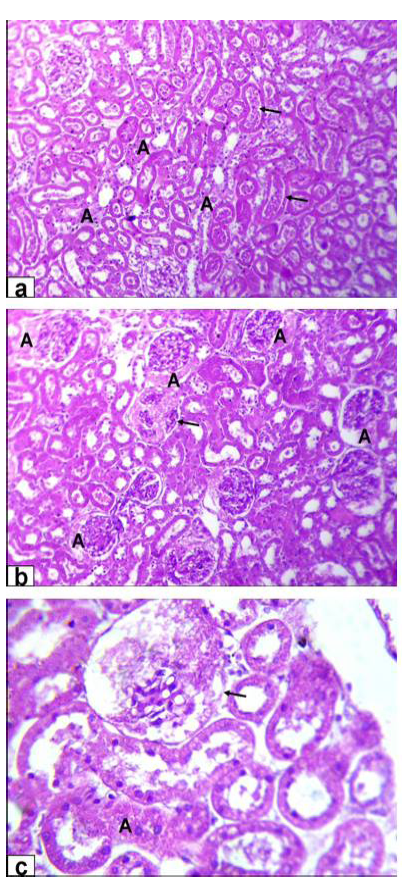
Photomicrographs of kidney sections stained with HE from rats treated with low dose of Aluminium chloride (2g/L); (a) tubular dilatation with cellular debris in its lumen (arrows) & tubular necrosis (A, X200); b) glomerulus’s filtrate occupied the space of bowman capsule (A) & necrosis of glomerulus’s tuft of bowman capsule (arrow, X200); c) necrosis of some renal tubules (A) and glomerulus’s tuft of bowman capsule (arrow, X200)
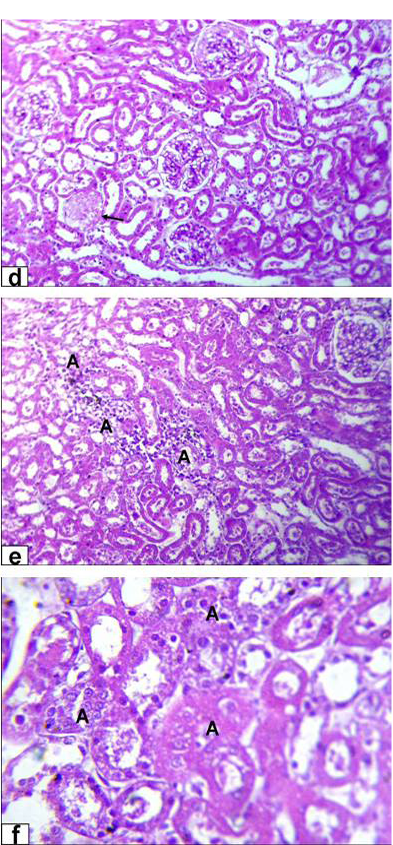
Photomicrographs of kidney sections stained with HE from rats treated with high dose of Aluminium chloride (3.5g/L) showing (d) complete necrosis of glomerulus’s tuft of bowman capsule (arrow, X200); e) interstitial nephritis with inflammatory cell infiltration (A, X200); f) tubular necrosis (A, X400)