Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
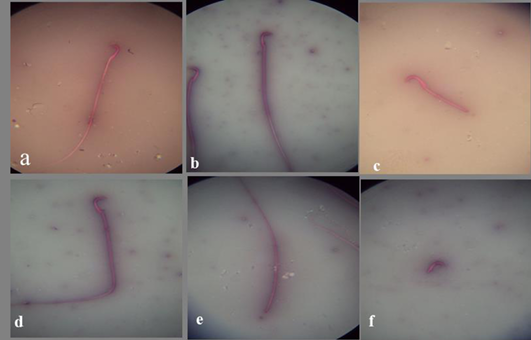
Figure 1: a) Spermatozoon of the control mature male albino rat showing normal sperm; b) Spermatozoon of the DMSO mature male albino rat showing normal sperm; c) Spermatozoon of treated mature male albino rat orally administrated crude extract of Euphorbia peplus at dose level of 500mg/kg b.wt. twice weekly for 65 days showing detached tail; d) bent tail; e) detached head; f) detached tail
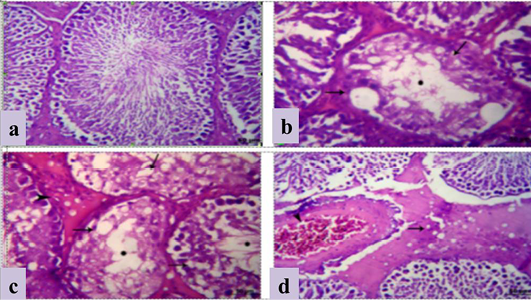
Figure 2: a) Section in Testis of Control mature albino rat showing normal germ cells of seminiferous tubules and Leydig cells; b, c) Section in testis of treated mature male albino rat orally administrated crude extract of Euphorbia peplus at dose level of 500mg/kg b.wt twice weekly for 65 days showing testicular degeneration which represented by atrophied irregular seminiferous tubules and vacuolation of its lining epithelia (arrows) besides incomplete spermatogenesis (*) and interstitial edema (arrowhead); d) interstitial edema (arrow), vacuolation of leydig cells and congested blood vessels; H&E (Bar=100μm).
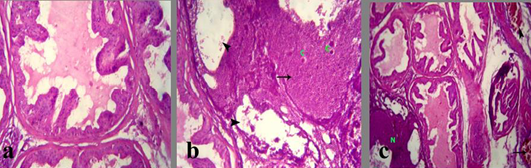
Figure 3: a) Section in prostate of Section in Prostate of the control mature male albino rat showing normal lobulation, lining epithelium and fluid in the lumen and acinar spaces; b) treated mature male albino rat orally administrated crude extract of Euphorbia peplus at dose level of 500mg/ kg b.wt twice weekly for 65 days showing area of necrosis (arrows), corpora amylacea (C) and cystic dilation of acini without secretory fluid (arrowheads); c) congested blood vessels (arrow) and hemorrhage (arrowhead) besides the necrotic area (N)
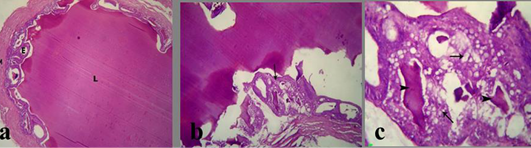
Figure 4: a) Section in Seminal vesicle of the control male albino rat showing normal lumen filled with eosinophilic fluid (L), secretory epithelium (E) and muscular coat (M); b, c) treated mature male albino rat orally administrated crude extract of Euphorbia peplus at dose level of 500mg/kg b.wt twice weekly for 65 days showing severe vacuolation of lining epithelium (arrows) and scanty insipisated secretion (arrowheads)