Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
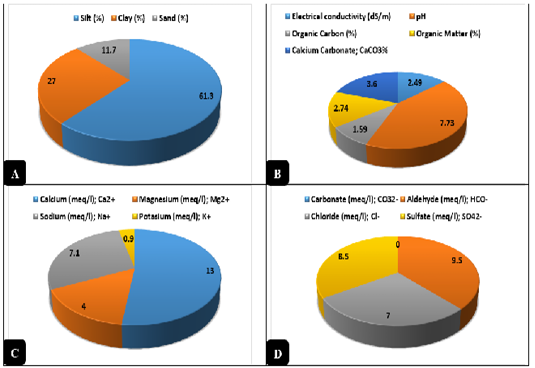
Physical and Chemical analysis of clay. A) Physical analysis of the natural clay (%). B) Chemical analysis of the natural clay. C) Cations contents of the natural clay expressed by meq/l. D) Anions contents of the natural clay expressed by meq/l.
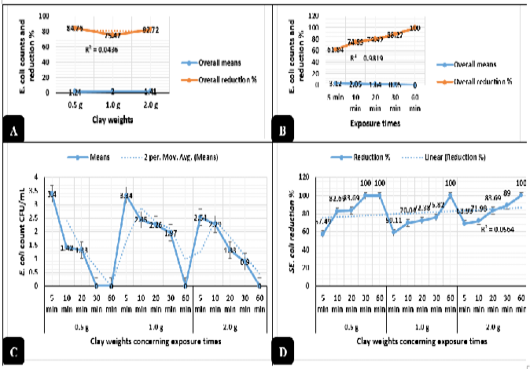
Antimicrobial action of natural clay on E. coli logarithmic counts during the in-vitro trials. A) Overall means of E. coli counts (CFU/mL) and reductions (%) concerning the clay weights. B) Overall means of E. coli counts (CFU/mL) and reductions (%) concerning the exposure times. C) E. coli counts (CFU/mL) concerning the clay weights and exposure times. D) E. coli reductions (%) concerning the clay weights and exposure times.
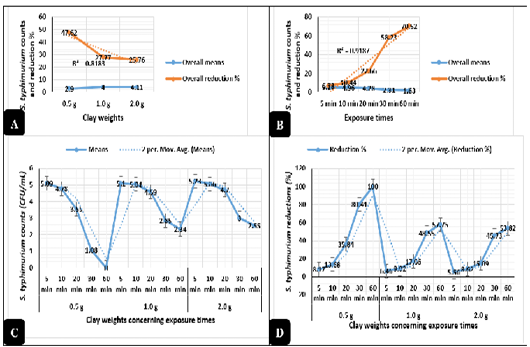
Antimicrobial action of natural clay on Salmonella typhimurium logarithmic counts during the in-vitro trials. A) Overall means of Salmonella typhimurium counts (CFU/mL) and reductions (%) concerning the clay weights. B) Overall means of Salmonella typhimurium counts (CFU/mL) and reductions (%) concerning the exposure times. C) Salmonella typhimurium counts (CFU/mL) concerning the clay weights and exposure times. D) Salmonella typhimurium reductions (%) concerning the clay weights and exposure times.