Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
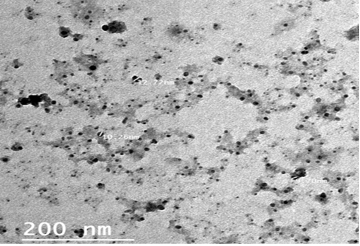
Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of the Propolis-ALg NPs.
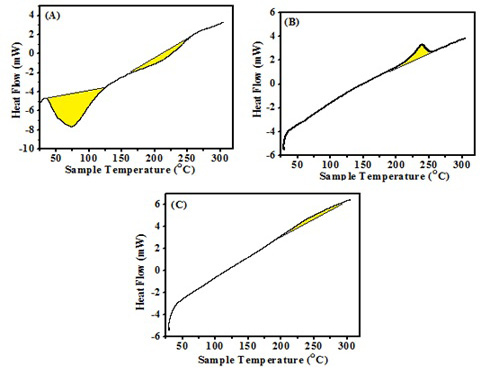
DSC thermogram of (A) Propolis, (B) ALg NPs and (C) ALg-Propolis NPs.
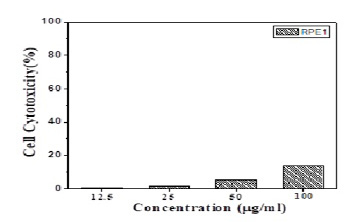
In-vitro cytotoxicity of the Propolis- ALg NPs in normal retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE1).
Lumpy skin disease viral in the shoulder of a cow 2 years old- 2 cm in diameter- a photo: (A) before treatment and (B) after treatment with Alginate-Propolis NPs.
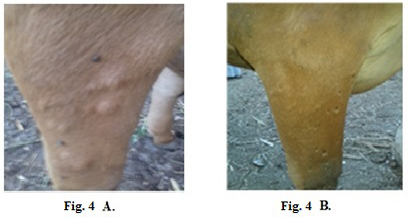
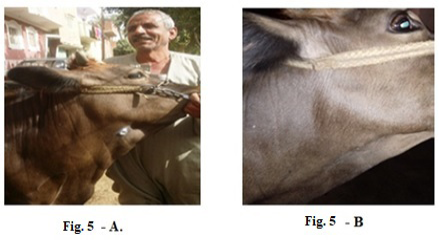
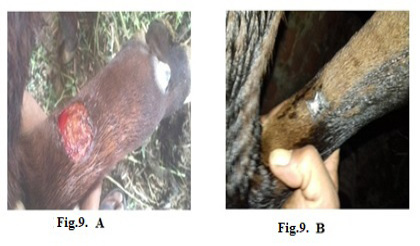
Lumpy skin disease viral in the submaxillary space of a cow 5 years old -2 cm in diameter- a photo: (A) before treatment and (B) after treatment with Alginate-Propolis NPs spray.
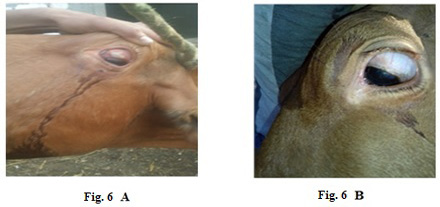
Lumpy skin disease viral in the eye of a cow 4 years old- 1 cm in diameter- a photo:
(A) before treatment and (B) after treatment with challenged ALg-Propolis NPs eye drops.
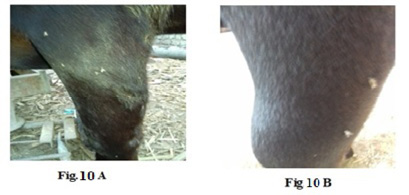
Lumpy skin disease viral in the leg of a cow 6 years old -1cm in diameter - a photo: (A) before treatment and (B) after treatment with challenged ALg-Propolis NPs spray.
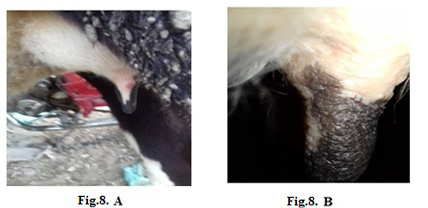
Lumpy skin disease viral in the teat of a cow 5 years old-1 cm in diameter- a photo: (A) before treatment and (B) after treatment with challenged ALg-Propolis NPs spray.
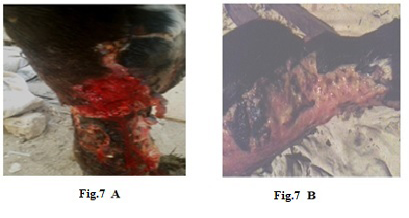
Lumpy skin disease viral in the forelimb of a young cow 1-year-old- 4 cm in diameter- a photo: (A) before treatment and (B) after treatment with challenged ALg-Propolis NPs spray.
Lumpy skin disease viral Oedema in the forelimb of a cow 4 years old - a photo: (A) before treatment and (B) after treatment with challenged ALg-Propolis NPs.