Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
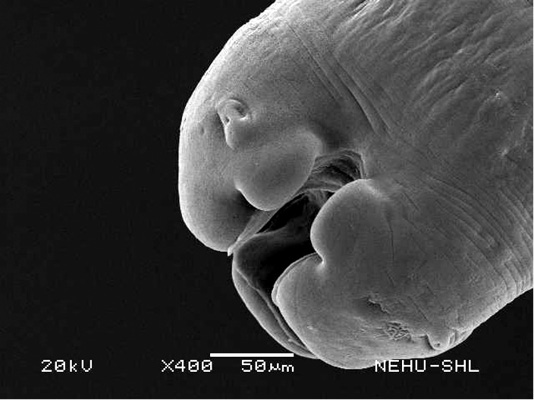
Scanning electron microscopy of the anterior part of an untreated (normal) A. galli. Three lips are seen at the bottom. The central hollow area is the mouth. On two lips are small eye-like papillae.
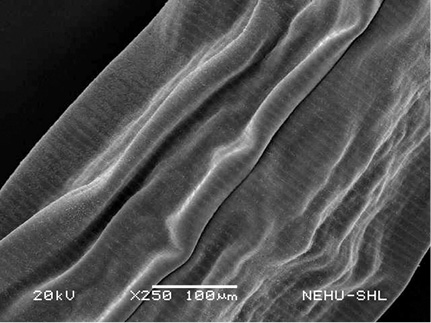
Scanning electron microscopy of the main body of an untreated (normal) A. galli. The cylindrical body consists of a series of transverse lines called annulations.
Scanning electron microscopy of the anterior part of A. galli treated with PZQ/PTP. Deflation and distortion of the lips are prominent.
Scanning electron microscopy of the main body of A. galli treated with PZQ/PTP. Large longitudinal folds are seen on the cuticle.
Scanning electron microscopy of the tail end of A. galli treated with PZQ/PTP. The tail is deflated. A small terminal spine is seen at the tip.
Scanning electron microscopy of the anterior part of A. galli treated with ABZ. The lips are deflated, shrunken and surrounded by contracted cuticle.
Scanning electron microscopy of the main body of A. galli treated with ABZ. The cuticle developed short but many longitudinal folds.
Scanning electron microscopy of the tail end of A. galli treated with ABZ. Deflation is very slight but cuticular folds can be seen. The terminal spine is intact.