Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
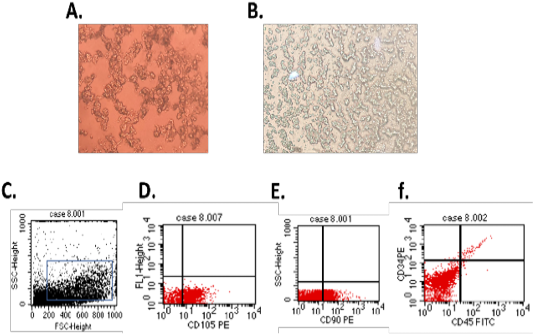
(A.) Br-MSCs isolation 3rd day of culture showed rounded and elongated nucleus (B.) 7th day of culture cells showed typical fibroblastic appearance. Br-MSCs flow cytometrical identification (C.: F.) (C.) side scatter and forward scatter gated Br-MSCs cells, (D.) gated Br-MSCS cell population were positive for CD105, (E.) gated Br-MSCS cell population were positive for CD90 (F.) gated Br-MSCS cell population were negative for hematopoietic stem cell surface marker (CD34, CD45).
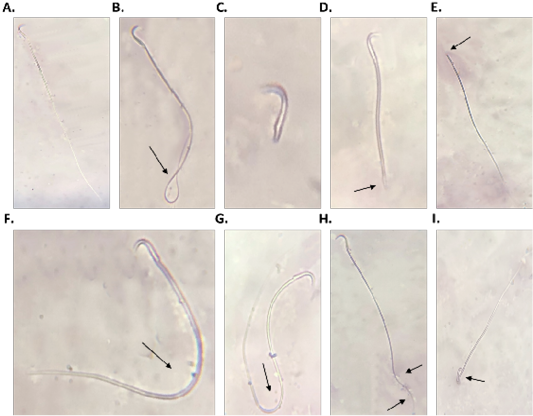
Sperm morphology (A.: I.), A. normal sperm, B. looped tail sperm, C. detached tail sperm, D. stunt sperm, E. detached head, F. and G. bent tail H. curved tail sperm, I. broken head.
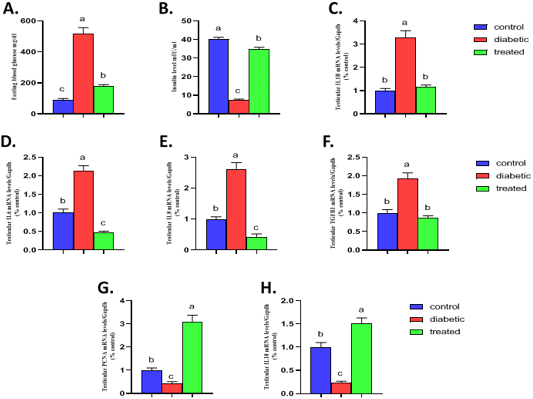
Effect of Br-MSCs administration on blood glucose level, serum insulin level and testicular immune profile of type 1 induced diabetic rat (A-H). A. fasting blood glucose level, B. serum insulin level and RT-PCR analysis for relative mRNA expression of; C. IL1β, D. IL6, E. IL8, F. TGFβ1, G. PCNA and H. IL10 gene in testicular tissue. Means bearing different superscripts were significantly different at P < 0.05. Abbreviations; IL (interleukin), TGFβ1 (Transforming growth factor beta 1), PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) Gapdh (Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase).
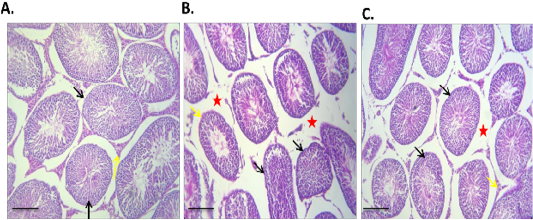
effect of Br-MSCs administration on testis morphometry of type 1 induced diabetic rats (A – C): A. Photomicrograph of testes showing normal testicular tissue with preserved seminiferous tubules (black arrow) and leydig cells (yellow arrow) HandE X 100, B. Photomicrograph of testes showing, sever tubular atrophy (black arrow), edema (red star) and partially atrophied tubules (yellow arrows) HandE X 100, C. Photomicrograph of diabetic Br-MSCs treated rats testes showing mild to moderate interstitial edema (red star) with normal tubules appears normal with functional spermatogenesis, spermiogenesis (yellow arrows) and hypertrophied leydig cell (red arrow), HandE X 100.