Journal of Animal Health and Production
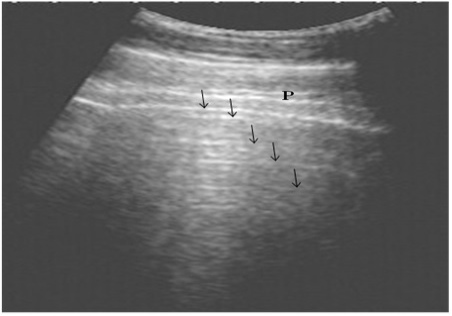
Ultrasonography of the normal lung in healthy cows using a 3.5 MHz transducer. The pleural layers appear as white linear echogenic lines. Reverberation artifacts appear as echogenic lines parallel to the pulmonary surface (Arrows). P is the parietal and visceral pleura.
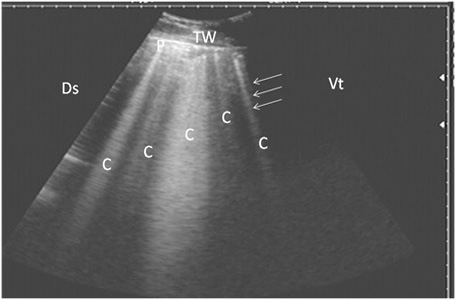
Ultrasonography of pulmonary emphysema in 9 cows using a 3.5 MHz transducer. The image shows multiple comet-tail artifacts in the form of bright echogenic bands (white arrows, C), pleura (P) and the thoracic wall (TW). The right part of the image is ventral (Vt) and the left is dorsal (Ds).
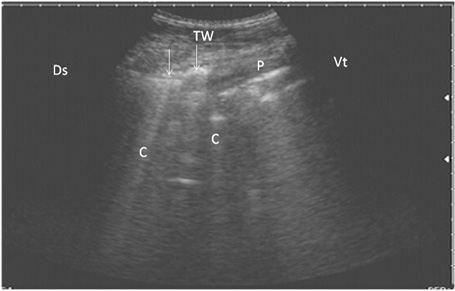
Ultrasonography of bronchopneumonia in cows using a 3.5 MHz transducer. The image shows small hypoechoic circular zones at the lung surface with a comet-tail artifact (white arrows, C), pleura (P) and the thoracic wall (TW). The right part of the image is ventral (Vt) and the left is dorsal (Ds).
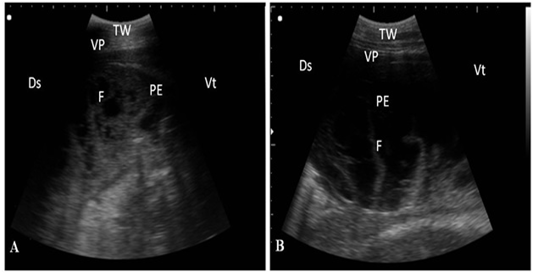
Ultrasonography of pleurisy in cows using a 3.5 MHz transducer. (A) The image shows the presence of thick fragmented visceral pleura and pleural sac filled with echogenic fibrin shreds and anechoic exudates. (B) The image shows pleural effusion and echogenic fibrin shreds. Visceral pleura (VP), fibrin (F), pleural effusion (PE), and the thoracic wall (TW). The right part of the image is ventral (Vt) and the left is dorsal (Ds).
Ultrasonography of the lung of a diseased cow using a 3.5 MHz transducer. The image shows hypoechoic fluid in the pleural cavity with echogenic bands that were hyperechoic with comet-tail artifacts. Pleura (P), fibrin (F), pleural effusion (PE), and the thoracic wall (TW). The right part of the image is ventral (Vt) and the left is dorsal (Ds).